An exploratory, randomized, parallel-group, open-label, relative bioavailability study with an additional two-period crossover food-effect study exploring the pharmacokinetics of two novel formulations of pexmetinib (ARRY-614)
- PMID: 26491375
- PMCID: PMC4598228
- DOI: 10.2147/CPAA.S83871
An exploratory, randomized, parallel-group, open-label, relative bioavailability study with an additional two-period crossover food-effect study exploring the pharmacokinetics of two novel formulations of pexmetinib (ARRY-614)
Abstract
Background: Pexmetinib (ARRY-614) is a dual inhibitor of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase and Tie2 signaling pathways implicated in the pathogenesis of myelodysplastic syndromes. Previous clinical experience in a Phase I dose-escalation study of myelodysplastic syndrome patients using pexmetinib administered as neat powder-in-capsule (PIC) exhibited high variability in pharmacokinetics and excessive pill burden, prompting an effort to improve the formulation of pexmetinib.
Methods: A relative bioavailability assessment encompassed three parallel treatment cohorts of unique subjects comparing the two new formulations (12 subjects per cohort), a liquid oral suspension (LOS) and liquid-filled capsule (LFC) and the current clinical PIC formulation (six subjects) in a fasted state. The food-effect assessment was conducted as a crossover of the LOS and LFC formulations administered under fed and fasted conditions. Subjects were divided into two groups of equal size to evaluate potential period effects on the food-effect assessment.
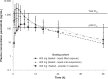
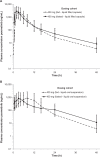
Results: The geometric mean values of the total plasma exposures based upon area-under-the-curve to the last quantifiable sample (AUClast) of pexmetinib were approximately four- and twofold higher after administration of the LFC and LOS formulations, respectively, than after the PIC formulation, when the formulations were administered in the fasted state. When the LFC formulation was administered in the fed state, pexmetinib AUClast decreased by <5% compared with the fasted state. After administration of the LOS formulation in the fed state, pexmetinib AUClast was 34% greater than observed in the fasted state.
Conclusion: These results suggest that the LFC formulation of pexmetinib may achieve greater exposures with lower doses due to the greater bioavailability compared to the PIC, and remain unaffected by coadministration with food.
Keywords: bioavailability; food-effect; formulation; liquid-filled capsule; myelodysplastic syndromes; pexmetinib.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparison of the Pharmacokinetics of the Phase II and Phase III Capsule Formulations of Selumetinib and the Effects of Food on Exposure: Results From Two Randomized Crossover Trials in Healthy Male Subjects.Clin Ther. 2017 Nov;39(11):2260-2275.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2017.08.022. Epub 2017 Oct 4. Clin Ther. 2017. PMID: 28985960 Clinical Trial.
-
A Phase I, open-label, randomized, crossover study in healthy subjects to evaluate the bioavailability of, and the food effect on, a pomalidomide oral liquid suspension.Clin Pharmacol. 2018 Jul 19;10:89-99. doi: 10.2147/CPAA.S171735. eCollection 2018. Clin Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 30050331 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of food on the pharmacokinetics of oxycodone and naltrexone from ALO-02, an extended release formulation of oxycodone with sequestered naltrexone.Clin Pharmacol Drug Dev. 2015 Sep;4(5):370-6. doi: 10.1002/cpdd.177. Epub 2015 Jan 22. Clin Pharmacol Drug Dev. 2015. PMID: 27137146 Clinical Trial.
-
Bioavailability and Pharmacokinetics of TRPV1 Antagonist Mavatrep (JNJ-39439335) Tablet and Capsule Formulations in Healthy Men: Two Open-Label, Crossover, Single-Dose Phase 1 Studies.Clin Pharmacol Drug Dev. 2018 Sep;7(7):699-711. doi: 10.1002/cpdd.412. Epub 2017 Nov 10. Clin Pharmacol Drug Dev. 2018. PMID: 29125700 Clinical Trial.
-
Evaluation of the effect of new formulation, food, or a proton pump inhibitor on the relative bioavailability of the smoothened inhibitor glasdegib (PF-04449913) in healthy volunteers.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2017 Dec;80(6):1249-1260. doi: 10.1007/s00280-017-3472-9. Epub 2017 Oct 30. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 29086063 Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
Functional Roles of JNK and p38 MAPK Signaling in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jan 20;23(3):1108. doi: 10.3390/ijms23031108. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35163030 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Repurposing pexmetinib as an inhibitor of TKI-resistant BCR::ABL1.Leukemia. 2024 Aug;38(8):1843-1847. doi: 10.1038/s41375-024-02282-y. Epub 2024 May 15. Leukemia. 2024. PMID: 38750137 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Steensma DP, Tefferi A. The myelodysplastic syndrome(s): a perspective and review highlighting current controversies. Leuk Res. 2003;27(2):95–120. - PubMed
-
- Nimer SD. Myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood. 2008;111(10):4841–4851. - PubMed
-
- Sokol L, Cripe L, Kantarjian H, Sekeres MA, Parmar S, Greenberg P. Randomized, dose-escalation study of the p38alpha MAPK inhibitor SCIO-469 in patients with myelodysplastic syndrome. Leukemia. 2013;27(4):977–980. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

