Level of Adherence to Prophylactic Osteoporosis Medication amongst Patients with Polymyalgia Rheumatica and Giant Cell Arteritis: A Cross-Sectional Study
- PMID: 26491449
- PMCID: PMC4603323
- DOI: 10.1155/2015/783709
Level of Adherence to Prophylactic Osteoporosis Medication amongst Patients with Polymyalgia Rheumatica and Giant Cell Arteritis: A Cross-Sectional Study
Abstract
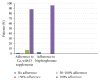
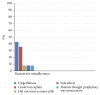
Objective. To estimate level of adherence to oral calcium and vitamin D supplementation as well as bisphosphonate amongst patients with PMR and GCA treated with glucocorticoids. Method. A total of 138 patients with the diagnosis of PMR and/or GCA registered in our department in December 2013. In this cross-sectional study we interviewed all the patients to measure level of adherence to calcium and vitamin D, as well as bisphosphonates. Results. Out of the 118 included patients, 88.9% of them were adherent to their prescription. Only 2 patients (1.7%) did not take calcium and vitamin D at all and 10 patients (8.5%) took their medication infrequently, 9 and 1 out of 10 patients took the medication 50-100% of the time and less than 50% of the prescribed dose, respectively. Sixty-one patients received additional treatment with bisphosphonate and 96.6% were adherent to this therapy. The remaining 3.4% of the patients did not take the medication at all. Forgetfulness, adverse side effects, and lack of understanding of treatment benefits were the most significant causes for nonadherence to calcium and vitamin D. Conclusions. Contrary to what we expected this study found that adherence to osteoporosis preventive medication in patients with PMR and GCA was high.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Long-term glucocorticoid treatment in patients with polymyalgia rheumatica, giant cell arteritis, or both diseases: results from a national rheumatology database.Rheumatol Int. 2018 Apr;38(4):569-577. doi: 10.1007/s00296-017-3874-3. Epub 2017 Nov 9. Rheumatol Int. 2018. PMID: 29124397
-
[Polymyalgia rheumatica and temporal arteritis].Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd. 2005 Aug 27;149(35):1932-7. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd. 2005. PMID: 16159030 Review. Dutch.
-
Homocysteine levels in polymyalgia rheumatica and giant cell arteritis: influence of corticosteroid therapy.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2003 Sep;42(9):1055-61. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keg293. Epub 2003 Apr 16. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2003. PMID: 12730520
-
[Polymyalgia rheumatica and Giant Cell Arteritis - Update on Diagnosis and Therapy].Praxis (Bern 1994). 2020;109(5):347-354. doi: 10.1024/1661-8157/a003444. Praxis (Bern 1994). 2020. PMID: 32233763 German.
-
Glucocorticoids for Management of Polymyalgia Rheumatica and Giant Cell Arteritis.Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 2016 Feb;42(1):75-90, viii. doi: 10.1016/j.rdc.2015.08.009. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 2016. PMID: 26611552 Review.
Cited by
-
Prognostic impacts of glucocorticoid treatment in patients with polymyalgia rheumatica and giant cell arteritis.Sci Rep. 2021 Mar 18;11(1):6220. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-85857-4. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33737697 Free PMC article.
-
Initiation of anti-osteoporotic drugs in high-risk female patients starting glucocorticoid treatment: a population study in Norway.Arch Osteoporos. 2020 Aug 5;15(1):121. doi: 10.1007/s11657-020-00783-8. Arch Osteoporos. 2020. PMID: 32757143 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Caylor T. L., Perkins A. Recognition and management of polymyalgia rheumatica and giant cell arteritis. American Family Physician. 2013;88(10):676–684. - PubMed
-
- Unwin B., Williams C. M., Gilliland W. Polymyalgia rheumatica and giant cell arteritis. American Family Physician. 2006;74(9):1547–1557. - PubMed
-
- Lindberg M., Hoerslev-Petersen K. National Danish Guideline for Diagnosis and Treatment of Polymyalgia Rheumatica and Giant Cell Arteritis. 2008. http://www.danskreumatologiskselskab.dk/fileadmin/DRS/kliniskeretningsli....
-
- Duru N., van der Goes M. C., Jacobs J. W. G., et al. EULAR evidence-based and consensus-based recommendations on the management of medium to high-dose glucocorticoid therapy in rheumatic diseases. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases. 2013;72(12):1905–1913. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-203249. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources