Dna2 nuclease-helicase structure, mechanism and regulation by Rpa
- PMID: 26491943
- PMCID: PMC4716839
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.09832
Dna2 nuclease-helicase structure, mechanism and regulation by Rpa
Abstract
The Dna2 nuclease-helicase maintains genomic integrity by processing DNA double-strand breaks, Okazaki fragments and stalled replication forks. Dna2 requires ssDNA ends, and is dependent on the ssDNA-binding protein Rpa, which controls cleavage polarity. Here we present the 2.3 Å structure of intact mouse Dna2 bound to a 15-nucleotide ssDNA. The nuclease active site is embedded in a long, narrow tunnel through which the DNA has to thread. The helicase domain is required for DNA binding but not threading. We also present the structure of a flexibly-tethered Dna2-Rpa interaction that recruits Dna2 to Rpa-coated DNA. We establish that a second Dna2-Rpa interaction is mutually exclusive with Rpa-DNA interactions and mediates the displacement of Rpa from ssDNA. This interaction occurs at the nuclease tunnel entrance and the 5' end of the Rpa-DNA complex. Hence, it only displaces Rpa from the 5' but not 3' end, explaining how Rpa regulates cleavage polarity.
Keywords: DNA end resection; DNA replication; Dna2; Rpa; biophysics; chromosomes; genes; helicase; none; nuclease; structural biology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that no competing interests exist.
Figures
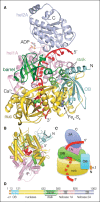

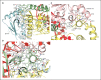
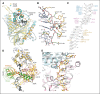
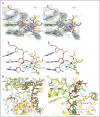

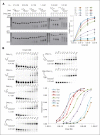

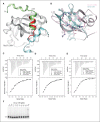

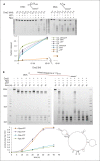
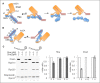
References
-
- Adams PD, Afonine PV, Bunkóczi Gábor, Chen VB, Davis IW, Echols N, Headd JJ, Hung L-W, Kapral GJ, Grosse-Kunstleve RW, Mccoy AJ, Moriarty NW, Oeffner R, Read RJ, Richardson DC, Richardson JS, Terwilliger TC, Zwart PH, et al. PHENIX : a comprehensive python-based system for macromolecular structure solution. Acta Crystallographica Section D Biological Crystallography. 2010;66:213–221. doi: 10.1107/S0907444909052925. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

