miRNA Stability in Frozen Plasma Samples
- PMID: 26492230
- PMCID: PMC6331950
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules201019030
miRNA Stability in Frozen Plasma Samples
Abstract
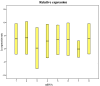
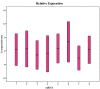
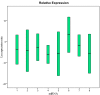
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) represent a family of small non-coding ribonucleic acids that post-transcriptionally inhibits the expression of their target messenger RNAs (mRNAs), thereby acting as general gene repressors. In this study we examined the relative quantity and stability of miRNA subjected to a long period of freezing; we compared the stability of eight miRNAs in the plasma of five human healthy controls before freezing and after six and 12 months of storage at -80 °C. In addition, we examined the plasma frozen for 14 years and the amount of miRNA still available. Using a Life Technologies protocol to amplify and quantify plasma miRNAs from EDTA (Ethylene Diamine Tetraacetic Acid)-treated blood, we analyzed the stability of eight miRNAs, (miR-125b-5p, miR-425-5p, miR-200b-5p, miR-200c-3p, miR-579-3p, miR-212-3p, miR-126-3p, and miR-21-5p). The miRNAs analyzed showed a high stability and long frozen half-life.
Keywords: long freezing times; miRNA; sequences AU or UA; stability.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

