Longitudinal Study of Cytokine Expression, Lipid Profile and Neuronal Growth Factors in Human Breast Milk from Term and Preterm Deliveries
- PMID: 26492267
- PMCID: PMC4632435
- DOI: 10.3390/nu7105415
Longitudinal Study of Cytokine Expression, Lipid Profile and Neuronal Growth Factors in Human Breast Milk from Term and Preterm Deliveries
Abstract
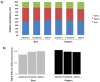
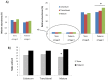
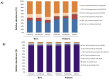
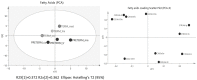
Breast milk (BM) is considered as a reference for infant nutrition. The role of bioactive components, such as cytokines, hormones, growth factors (GFs) and fatty acids (FAs) is poorly known, but they might be implicated in immune response development. The aim of this study was to identify the lipid profile and the spectrum of cytokines and neuronal GF in BM samples and analyse the influence of gestational age and lactation time on these components. This study used a longitudinal prospective method for the characterization of cytokines, FAs and GFs global profiles in 120 BM samples from 40 healthy mothers (20 preterm and 20 term) collected as colostrum, transitional and mature milk. The cytokines were analysed by protein array (Ray Bio® Human Cytokine Array G6. Ray Biotech, Inc. Norcross, GA, USA) and the FAs were analysed by gas chromatography. The FA profile was similar between the term and the preterm BM samples. Omega-3-α-linoleic and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) and omega-6-linoleic acid were the most abundant in the term and preterm samples during lactation. Omega-3 ETA and omega-3 EPA we observed exclusively in the preterm samples. The cytokine profile showed a different trend based on gestational age. A significantly higher expression of neurotrophic factors was found in the mature preterm milk samples as compared to the mature term samples. Our study is the first to identify the influence and interactions of perinatal factors on cytokine, GFs and FAs in human milk.
Keywords: breast milk; breastfeeding; cytokines; docosahexaenoic acid; fatty acids; growth factors; human milk; neurotrophic factor; polyunsaturated fatty acids.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Temporal Progression of Fatty Acids in Preterm and Term Human Milk of Mothers from Switzerland.Nutrients. 2019 Jan 8;11(1):112. doi: 10.3390/nu11010112. Nutrients. 2019. PMID: 30626044 Free PMC article.
-
[Fatty acid composition of human milk in mothers of preterm and full-term infants in the first three weeks of lactation].Orv Hetil. 2006 Aug 6;147(31):1459-63. Orv Hetil. 2006. PMID: 16981419 Hungarian.
-
Human milk fatty acid profile across lactational stages after term and preterm delivery: A pooled data analysis.Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 2020 May;156:102023. doi: 10.1016/j.plefa.2019.102023. Epub 2019 Oct 16. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 2020. PMID: 31699594 Review.
-
Long chain fatty acids and related pro-inflammatory, specialized pro-resolving lipid mediators and their intermediates in preterm human milk during the first month of lactation.Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 2017 Jun;121:1-6. doi: 10.1016/j.plefa.2017.05.003. Epub 2017 May 18. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 2017. PMID: 28651692
-
Nutrition, growth, and allergic diseases among very preterm infants after hospital discharge.Dan Med J. 2013 Feb;60(2):B4588. Dan Med J. 2013. PMID: 23461996 Review.
Cited by
-
Modulation of the Systemic Immune Response in Suckling Rats by Breast Milk TGF-β2, EGF and FGF21 Supplementation.Nutrients. 2020 Jun 24;12(6):1888. doi: 10.3390/nu12061888. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 32599899 Free PMC article.
-
Source of human milk (mother or donor) is more important than fortifier type (human or bovine) in shaping the preterm infant microbiome.Cell Rep Med. 2022 Sep 20;3(9):100712. doi: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2022.100712. Epub 2022 Aug 26. Cell Rep Med. 2022. PMID: 36029771 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Donor Human Milk Update: Evidence, Mechanisms, and Priorities for Research and Practice.J Pediatr. 2017 Jan;180:15-21. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2016.09.027. Epub 2016 Oct 20. J Pediatr. 2017. PMID: 27773337 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Cytokines and Chemokines in Breastmilk of SARS-CoV-2 Infected or COVID-19 Vaccinated Mothers.Vaccines (Basel). 2022 Nov 24;10(12):2001. doi: 10.3390/vaccines10122001. Vaccines (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36560410 Free PMC article.
-
Immediate Pre-Partum SARS-CoV-2 Status and Immune Profiling of Breastmilk: A Case-Control Study.Front Immunol. 2021 Jul 26;12:720716. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.720716. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34381462 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lawrence R.A., Lawrence R.M. Host-resistance factors and immunologic significance of human milk. In: Lawrence R.A., Lawrence R.M., editors. Breastfeeding: A Guide for Medical Profession. 7th ed. Elsevier; Mosby, MO, USA: 2011. pp. 153–195.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

