Fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab treatment achieves long-term disease-free survival in IGHV-mutated chronic lymphocytic leukemia
- PMID: 26492934
- PMCID: PMC4760129
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2015-09-667675
Fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab treatment achieves long-term disease-free survival in IGHV-mutated chronic lymphocytic leukemia
Abstract
Accurate identification of patients likely to achieve long-progression-free survival (PFS) after chemoimmunotherapy is essential given the availability of less toxic alternatives, such as ibrutinib. Fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab (FCR) achieved a high response rate, but continued relapses were seen in initial reports. We reviewed the original 300 patient phase 2 FCR study to identify long-term disease-free survivors. Minimal residual disease (MRD) was assessed posttreatment by a polymerase chain reaction-based ligase chain reaction assay (sensitivity 0.01%). At the median follow-up of 12.8 years, PFS was 30.9% (median PFS, 6.4 years). The 12.8-year PFS was 53.9% for patients with mutated immunoglobulin heavy chain variable (IGHV) gene (IGHV-M) and 8.7% for patients with unmutated IGHV (IGHV-UM). 50.7% of patients with IGHV-M achieved MRD-negativity posttreatment; of these, PFS was 79.8% at 12.8 years. A plateau was seen on the PFS curve in patients with IGHV-M, with no relapses beyond 10.4 years in 42 patients (total follow-up 105.4 patient-years). On multivariable analysis, IGHV-UM (hazard ratio, 3.37 [2.18-5.21]; P < .001) and del(17p) by conventional karyotyping (hazard ratio, 7.96 [1.02-61.92]; P = .048) were significantly associated with inferior PFS. Fifteen patients with IGHV-M had 4-color MRD flow cytometry (sensitivity 0.01%) performed in peripheral blood, at a median of 12.8 years posttreatment (range, 9.5-14.7). All were MRD-negative. The high rate of very long-term PFS in patients with IGHV-M after FCR argues for the continued use of chemoimmunotherapy in this patient subgroup outside clinical trials; alternative strategies may be preferred in patients with IGHV-UM, to limit long-term toxicity.
© 2016 by The American Society of Hematology.
Figures
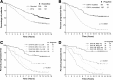
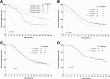
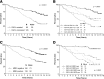

Comment in
-
Can FCR be curative in CLL?Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2015 Dec;12(12):684. doi: 10.1038/nrclinonc.2015.206. Epub 2015 Nov 17. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2015. PMID: 26573420 No abstract available.
-
Cure for CLL?Blood. 2016 Jan 21;127(3):274. doi: 10.1182/blood-2015-11-678532. Blood. 2016. PMID: 26796105 No abstract available.
References
-
- Hallek M, Fischer K, Fingerle-Rowson G, et al. International Group of Investigators; German Chronic Lymphocytic Leukaemia Study Group. Addition of rituximab to fludarabine and cyclophosphamide in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukaemia: a randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2010;376(9747):1164–1174. - PubMed
-
- Zenz T, Eichhorst B, Busch R, et al. TP53 mutation and survival in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28(29):4473–4479. - PubMed
-
- Dreger P. Allotransplantation for chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2009;2009(1):602–609. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

