Molecular and phylogenetic characterization of the homoeologous EPSP Synthase genes of allohexaploid wheat, Triticum aestivum (L.)
- PMID: 26492960
- PMCID: PMC4619226
- DOI: 10.1186/s12864-015-2084-1
Molecular and phylogenetic characterization of the homoeologous EPSP Synthase genes of allohexaploid wheat, Triticum aestivum (L.)
Abstract
Background: 5-Enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate synthase (EPSPS) is the sixth and penultimate enzyme in the shikimate biosynthesis pathway, and is the target of the herbicide glyphosate. The EPSPS genes of allohexaploid wheat (Triticum aestivum, AABBDD) have not been well characterized. Herein, the three homoeologous copies of the allohexaploid wheat EPSPS gene were cloned and characterized.
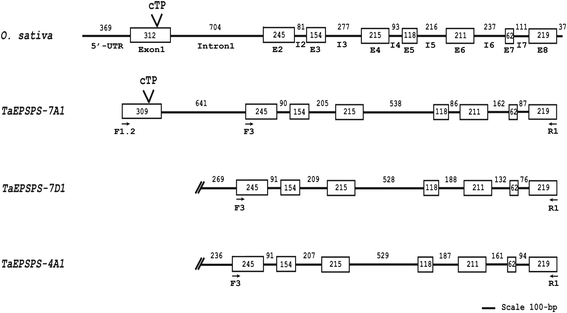
Methods: Genomic and coding DNA sequences of EPSPS from the three related genomes of allohexaploid wheat were isolated using PCR and inverse PCR approaches from soft white spring "Louise'. Development of genome-specific primers allowed the mapping and expression analysis of TaEPSPS-7A1, TaEPSPS-7D1, and TaEPSPS-4A1 on chromosomes 7A, 7D, and 4A, respectively. Sequence alignments of cDNA sequences from wheat and wheat relatives served as a basis for phylogenetic analysis.
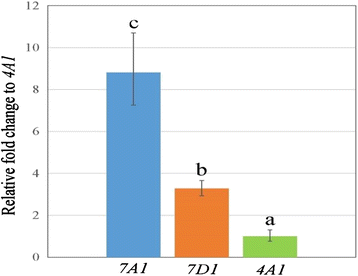
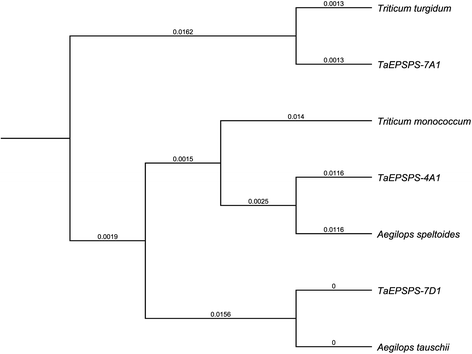
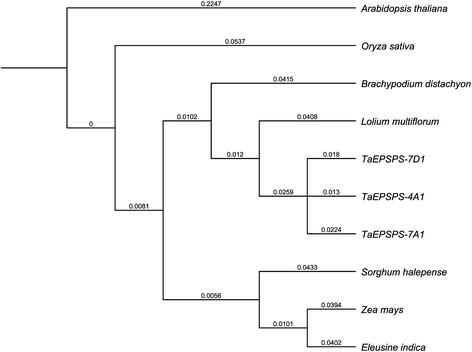
Results: The three genomic copies of wheat EPSPS differed by insertion/deletion and single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), largely in intron sequences. RT-PCR analysis and cDNA cloning revealed that EPSPS is expressed from all three genomic copies. However, TaEPSPS-4A1 is expressed at much lower levels than TaEPSPS-7A1 and TaEPSPS-7D1 in wheat seedlings. Phylogenetic analysis of 1190-bp cDNA clones from wheat and wheat relatives revealed that: 1) TaEPSPS-7A1 is most similar to EPSPS from the tetraploid AB genome donor, T. turgidum (99.7 % identity); 2) TaEPSPS-7D1 most resembles EPSPS from the diploid D genome donor, Aegilops tauschii (100 % identity); and 3) TaEPSPS-4A1 resembles EPSPS from the diploid B genome relative, Ae. speltoides (97.7 % identity). Thus, EPSPS sequences in allohexaploid wheat are preserved from the most two recent ancestors. The wheat EPSPS genes are more closely related to Lolium multiflorum and Brachypodium distachyon than to Oryza sativa (rice).
Conclusions: The three related EPSPS homoeologues of wheat exhibited conservation of the exon/intron structure and of coding region sequence, but contained significant sequence variation within intron regions. The genome-specific primers developed will enable future characterization of natural and induced variation in EPSPS sequence and expression. This can be useful in investigating new causes of glyphosate herbicide resistance.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Comparative sequence analysis of the phytochrome C gene and its upstream region in allohexaploid wheat reveals new data on the evolution of its three constituent genomes.Plant Mol Biol. 2005 Jul;58(5):625-41. doi: 10.1007/s11103-005-6801-z. Plant Mol Biol. 2005. PMID: 16158239
-
PCR-based landmark unique gene (PLUG) markers effectively assign homoeologous wheat genes to A, B and D genomes.BMC Genomics. 2007 May 30;8:135. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-8-135. BMC Genomics. 2007. PMID: 17535443 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-specific primer sets for starch biosynthesis genes in wheat.Theor Appl Genet. 2004 Oct;109(6):1295-1302. doi: 10.1007/s00122-004-1743-4. Theor Appl Genet. 2004. PMID: 15340684
-
Making the Bread: Insights from Newly Synthesized Allohexaploid Wheat.Mol Plant. 2015 Jun;8(6):847-59. doi: 10.1016/j.molp.2015.02.016. Epub 2015 Mar 5. Mol Plant. 2015. PMID: 25747845 Review.
-
Broadening the bread wheat D genome.Theor Appl Genet. 2019 May;132(5):1295-1307. doi: 10.1007/s00122-019-03299-z. Epub 2019 Feb 10. Theor Appl Genet. 2019. PMID: 30739154 Review.
Cited by
-
First Case of Glyphosate Resistance in Bromus catharticus Vahl.: Examination of Endowing Resistance Mechanisms.Front Plant Sci. 2021 Feb 18;12:617945. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.617945. eCollection 2021. Front Plant Sci. 2021. PMID: 33679832 Free PMC article.
-
Development of non-transgenic glyphosate tolerant wheat by TILLING.PLoS One. 2021 Sep 15;16(9):e0245802. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0245802. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34525118 Free PMC article.
-
gRNA validation for wheat genome editing with the CRISPR-Cas9 system.BMC Biotechnol. 2019 Oct 30;19(1):71. doi: 10.1186/s12896-019-0565-z. BMC Biotechnol. 2019. PMID: 31684940 Free PMC article.
-
MSB2-activated pheromone pathway regulates fungal plasma membrane integrity in response to herbicide adjuvant.Sci Adv. 2025 Feb 28;11(9):eadt8715. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adt8715. Epub 2025 Feb 28. Sci Adv. 2025. PMID: 40020065 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and Expression Analysis of EPSPS and BAR Families in Cotton.Plants (Basel). 2023 Sep 23;12(19):3366. doi: 10.3390/plants12193366. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37836107 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Geiger DR, Fuchs MA. Inhibitors of aromatic amino acid biosynthesis (glyphosate) In: Boger P, Wakabayashi K, Hirai K, editors. Herbicide classes in development: Mode of action, targets, genetic engineering, chemistry. New York: Springer; 2002. pp. 59–85.
-
- Cobb AH, Reade JPH. The inhibition of amino acid biosynthesis. In: Cobb AH, Reade JPH, editors. Herbicides and plant physiology. 2. New Jersey: Wiley-Blackwell; 2010. pp. 126–144.
-
- Ng CH, Wickneswari R, Salmijah S, Teng YT, Ismail BS. Gene polymorphisms in glyphosate-resistant and -susceptible biotypes of Eleusine indica from Malaysia. Weed Res. 2003;43:108–115. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-3180.2003.00322.x. - DOI
-
- Kaundun SS, Dale RP, Zelaya IA, Dinelli G, Marotti I, McIndoe E, et al. A novel P106L mutation in EPSPS and an unknown mechanism(s) act additively to confer resistance to glyphosate in a South African Lolium rigidum population. J Agric Food Chem. 2011;59:3227–3233. doi: 10.1021/jf104934j. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

