Predictive value and clinical utility of centrally assessed ER, PgR, and Ki-67 to select adjuvant endocrine therapy for premenopausal women with hormone receptor-positive, HER2-negative early breast cancer: TEXT and SOFT trials
- PMID: 26493064
- PMCID: PMC4749471
- DOI: 10.1007/s10549-015-3612-z
Predictive value and clinical utility of centrally assessed ER, PgR, and Ki-67 to select adjuvant endocrine therapy for premenopausal women with hormone receptor-positive, HER2-negative early breast cancer: TEXT and SOFT trials
Abstract
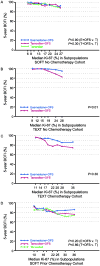
The SOFT and TEXT randomized phase III trials investigated adjuvant endocrine therapies for premenopausal women with hormone receptor-positive (HR+) early breast cancer. We investigated the prognostic and predictive value of centrally assessed levels of estrogen receptor (ER), progesterone receptor (PgR), and Ki-67 expression in women with HER2-negative disease. Of 5707 women enrolled, 4115 with HER2-negative (HR+/HER2-) disease had ER, PgR, and Ki-67 centrally assessed by immunohistochemistry. Breast cancer-free interval (BCFI) was defined from randomization to first invasive local, regional, or distant recurrence or contralateral breast cancer. The prognostic and predictive values of ER, PgR and Ki-67 expression levels were assessed using Cox modeling and STEPP methodology. In this HR+/HER2- population, the median ER, PgR, and Ki-67 expressions were 95, 90, and 18 % immunostained cells. As most patients had strongly ER-positive tumors, the predictive value of ER levels could not be investigated. Lower PgR and higher Ki-67 expression were associated with reduced BCFI. There was no consistent evidence of heterogeneity of the relative treatment effects according to PgR or Ki-67 expression levels, though there was a greater 5-year absolute benefit of exemestane + ovarian function suppression (OFS) versus tamoxifen with or without OFS at lower levels of PgR and higher levels of Ki-67. Women with poor prognostic features of low PgR and/or high Ki-67 have greater absolute benefit from exemestane + OFS versus tamoxifen + OFS or tamoxifen alone, but individually PgR and Ki-67 are of limited predictive value for selecting adjuvant endocrine therapy for premenopausal women with HR+/HER2- early breast cancer.
Keywords: Estrogen receptor; Exemestane; Ki-67; Ovarian function suppression; Progesterone receptor; Tamoxifen.
Conflict of interest statement
The remaining authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Regan MM, Pagani O, Fleming GF, Walley BA, Price KN, Rabaglio M, Maibach R, Ruepp B, Coates AS, Goldhirsch A, Colleoni M, Gelber RD, Francis PA. Adjuvant treatment of premenopausal women with endocrine-responsive early breast cancer: design of the TEXT and SOFT trials. Breast. 2013;22(6):1094–1100. doi: 10.1016/j.breast.2013.08.009. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Pagani O, Regan MM, Walley BA, Fleming GF, Colleoni M, Lang I, Gomez HL, Tondini C, Burstein HJ, Perez EA, Ciruelos E, Stearns V, Bonnefoi HR, Martino S, Geyer CE, Jr, Pinotti G, Puglisi F, Crivellari D, Ruhstaller T, Winer EP, Rabaglio-Poretti M, Maibach R, Ruepp B, Giobbie-Hurder A, Price KN, Bernhard J, Luo W, Ribi K, Viale G, Coates AS, Gelber RD, Goldhirsch A, Francis PA. Adjuvant exemestane with ovarian suppression in premenopausal breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2014;371(2):107–118. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1404037. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Francis PA, Regan MM, Fleming GF, Lang I, Ciruelos E, Bellet M, Bonnefoi HR, Climent MA, Da Prada GA, Burstein HJ, Martino S, Davidson NE, Geyer CE, Jr, Walley BA, Coleman R, Kerbrat P, Buchholz S, Ingle JN, Winer EP, Rabaglio-Poretti M, Maibach R, Ruepp B, Giobbie-Hurder A, Price KN, Colleoni M, Viale G, Coates AS, Goldhirsch A, Gelber RD. Adjuvant ovarian suppression in premenopausal breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2015;372(5):436–446. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1412379. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Viale G, Giobbie-Hurder A, Regan MM, Coates AS, Mastropasqua MG, Dell'Orto P, Maiorano E, MacGrogan G, Braye SG, Ohlschlegel C, Neven P, Orosz Z, Olszewski WP, Knox F, Thurlimann B, Price KN, Castiglione-Gertsch M, Gelber RD, Gusterson BA, Goldhirsch A. Prognostic and predictive value of centrally reviewed Ki-67 labeling index in postmenopausal women with endocrine-responsive breast cancer: results from Breast International Group Trial 1-98 comparing adjuvant tamoxifen with letrozole. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26(34):5569–5575. doi: 10.1200/jco.2008.17.0829. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Viale G, Regan MM, Maiorano E, Mastropasqua MG, Dell'Orto P, Rasmussen BB, Raffoul J, Neven P, Orosz Z, Braye S, Ohlschlegel C, Thurlimann B, Gelber RD, Castiglione-Gertsch M, Price KN, Goldhirsch A, Gusterson BA, Coates AS. Prognostic and predictive value of centrally reviewed expression of estrogen and progesterone receptors in a randomized trial comparing letrozole and tamoxifen adjuvant therapy for postmenopausal early breast cancer: BIG 1-98. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25(25):3846–3852. doi: 10.1200/jco.2007.11.9453. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U10-CA-69651/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10-CA-37377/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CA032102/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180821/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- A15955/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- U10-CA180821/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA016116/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U24 CA075362/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA069974/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA21115/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA75362/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA077202/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA077202/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA021115/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA012027/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10-CA-69974/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10-CA-12027/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA069651/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA032102/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA037377/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA16116/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

