An MRI-compatible platform for one-dimensional motion management studies in MRI
- PMID: 26493684
- PMCID: PMC6342555
- DOI: 10.1002/mrm.25903
An MRI-compatible platform for one-dimensional motion management studies in MRI
Abstract
Purpose: Abdominal MRI remains challenging because of respiratory motion. Motion compensation strategies are difficult to compare clinically because of the variability across human subjects. The goal of this study was to evaluate a programmable system for one-dimensional motion management MRI research.
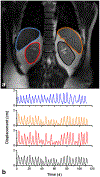
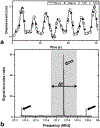
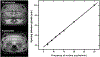
Methods: A system comprised of a programmable motorized linear stage and computer was assembled and tested in the MRI environment. Tests of the mutual interference between the platform and a whole-body MRI were performed. Organ trajectories generated from a high-temporal resolution scan of a healthy volunteer were used in phantom tests to evaluate the effects of motion on image quality and quantitative MRI measurements.
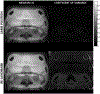
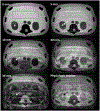
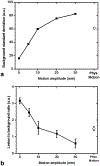
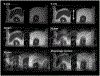
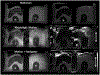
Results: No interference between the motion platform and the MRI was observed, and reliable motion could be produced across a wide range of imaging conditions. Motion-related artifacts commensurate with motion amplitude, frequency, and waveform were observed. T2 measurement of a kidney lesion in an abdominal phantom showed that its value decreased by 67% with physiologic motion, but could be partially recovered with navigator-based motion-compensation.
Conclusion: The motion platform can produce reliable linear motion within a whole-body MRI. The system can serve as a foundation for a research platform to investigate and develop motion management approaches for MRI. Magn Reson Med 76:702-712, 2016. © 2015 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Keywords: T2; abdominal MRI; breathing; motion; respiratory motion.
© 2015 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Phantoms for Quantitative Body MRI: a review and discussion of the phantom value.MAGMA. 2024 Aug;37(4):535-549. doi: 10.1007/s10334-024-01181-8. Epub 2024 Jun 19. MAGMA. 2024. PMID: 38896407 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Robust self-navigated body MRI using dense coil arrays.Magn Reson Med. 2016 Jul;76(1):197-205. doi: 10.1002/mrm.25858. Epub 2015 Jul 29. Magn Reson Med. 2016. PMID: 26220204 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of flexible body surface coil and patient table on PET quantification and image quality in integrated PET/MR.Nuklearmedizin. 2014;53(3):79-87. doi: 10.3413/Nukmed-0608-13-07. Epub 2014 Mar 21. Nuklearmedizin. 2014. PMID: 24658368
-
Continuously moving table MRI with golden angle radial sampling.Magn Reson Med. 2015 Dec;74(6):1690-7. doi: 10.1002/mrm.25531. Epub 2014 Dec 2. Magn Reson Med. 2015. PMID: 25461600 Free PMC article.
-
Compensation of breathing motion artifacts for MRI with continuously moving table.Magn Reson Med. 2010 Mar;63(3):701-12. doi: 10.1002/mrm.22162. Magn Reson Med. 2010. PMID: 20187180
Cited by
-
Breath-hold MR-HIFU hyperthermia: phantom and in vivo feasibility.Int J Hyperthermia. 2019;36(1):1084-1097. doi: 10.1080/02656736.2019.1679893. Int J Hyperthermia. 2019. PMID: 31707872 Free PMC article.
-
Design of a Patient-Specific Respiratory-Motion-Simulating Platform for In Vitro 4D Flow MRI.Ann Biomed Eng. 2023 May;51(5):1028-1039. doi: 10.1007/s10439-022-03117-6. Epub 2022 Dec 29. Ann Biomed Eng. 2023. PMID: 36580223
-
Design of a 6-DoF Parallel Robotic Platform for MRI Applications.J Med Robot Res. 2022 Jun-Sep;7(2-3):2241005. doi: 10.1142/s2424905x22410057. Epub 2022 Jun 27. J Med Robot Res. 2022. PMID: 37614779 Free PMC article.
-
Phantoms for Quantitative Body MRI: a review and discussion of the phantom value.MAGMA. 2024 Aug;37(4):535-549. doi: 10.1007/s10334-024-01181-8. Epub 2024 Jun 19. MAGMA. 2024. PMID: 38896407 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characterizing spatiotemporal information loss in sparse-sampling-based dynamic MRI for monitoring respiration-induced tumor motion in radiotherapy.Med Phys. 2016 Jun;43(6):2807-2820. doi: 10.1118/1.4948684. Med Phys. 2016. PMID: 27277029 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zech CJ, Herrmann KA, Huber A, Dietrich O, Stemmer A, Herzog P,Reiser MF, Schoenberg SO. High-resolution MR-imaging of the liver with T2-weighted sequences using integrated parallel imaging: comparison of prospective motion correction and respiratory triggering. J Magn Reson Imaging 2004;20:443–450. - PubMed
-
- Wang Y, Rossman PJ, Grimm RC, Wilman AH, Riederer SJ, Ehman RL.3D MR angiography of pulmonary arteries using real-time navigator gating and magnetization preparation. Magn Reson Med 1996;36:579–587. - PubMed
-
- Kohler MO, Denis de Senneville B, Quesson B, Moonen CT, Ries M.Spectrally selective pencil-beam navigator for motion compensation of MR-guided high-intensity focused ultrasound therapy of abdominal organs. Magn Reson Med 2011;66:102–111. - PubMed
-
- Nehrke K, Bornert P, Groen J, Smink J, Bock JC. On the performanceand accuracy of 2D navigator pulses. Magn Reson Imaging 1999;17: 1173–1181. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

