Soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitor enhances synaptic neurotransmission and plasticity in mouse prefrontal cortex
- PMID: 26494028
- PMCID: PMC4618874
- DOI: 10.1186/s12929-015-0202-7
Soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitor enhances synaptic neurotransmission and plasticity in mouse prefrontal cortex
Abstract
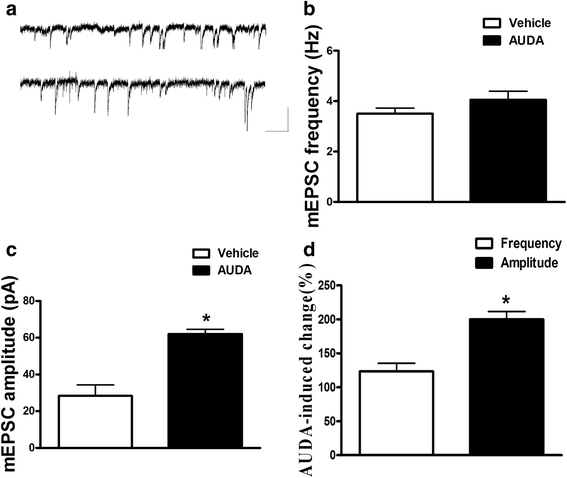
Background: The soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH) is an important enzyme chiefly involved in the metabolism of fatty acid signaling molecules termed epoxyeicosatrienoic acids (EETs). sEH inhibition (sEHI) has proven to be protective against experimental cerebral ischemia, and it is emerging as a therapeutic target for prevention and treatment of ischemic stroke. However, the role of sEH on synaptic function in the central nervous system is still largely unknown. This study aimed to test whether sEH C-terminal epoxide hydrolase inhibitor, 12-(3-adamantan-1-yl-ureido) dodecanoic acid (AUDA) affects basal synaptic transmission and synaptic plasticity in the prefrontal cortex area (PFC). Whole cell and extracellular recording examined the miniature excitatory postsynaptic currents (mEPSCs) and field excitatory postsynaptic potentials (fEPSPs); Western Blotting determined the protein levels of glutamate receptors and ERK phosphorylation in acute medial PFC slices.
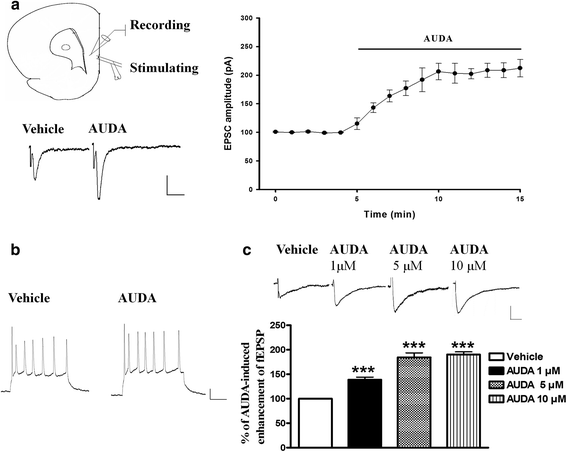
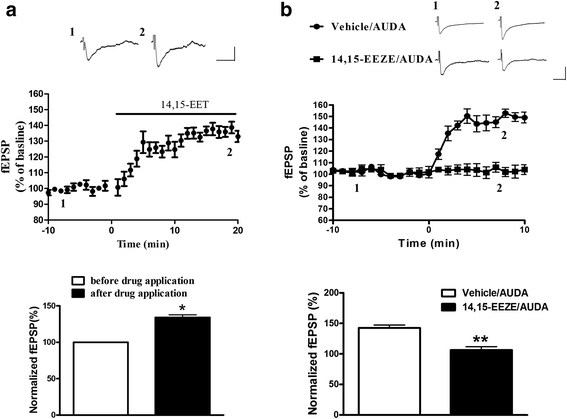
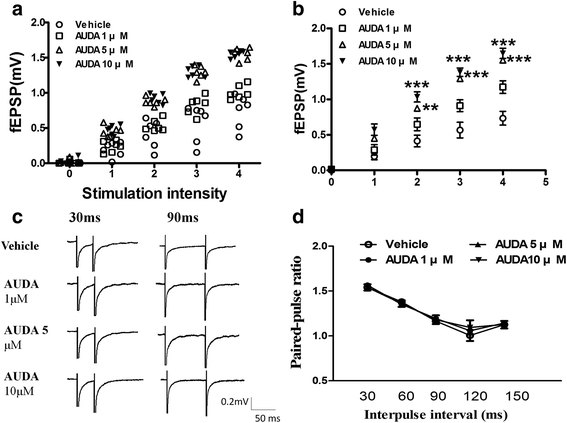
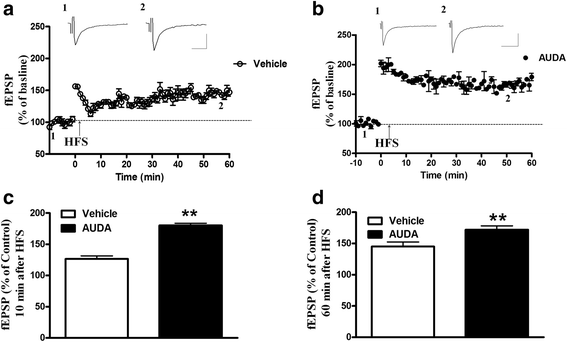
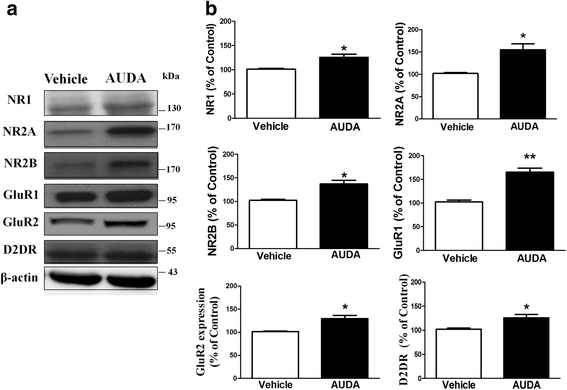
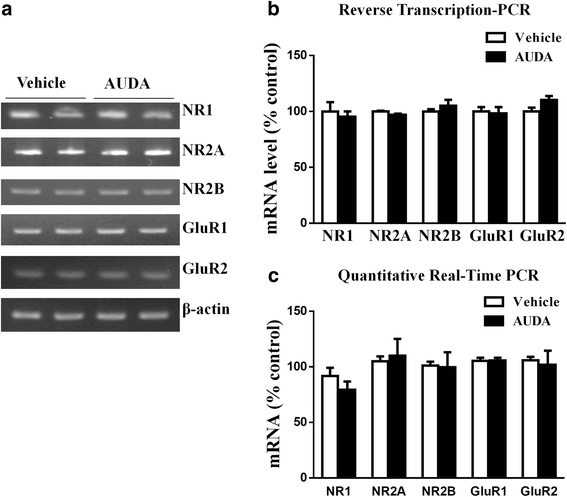
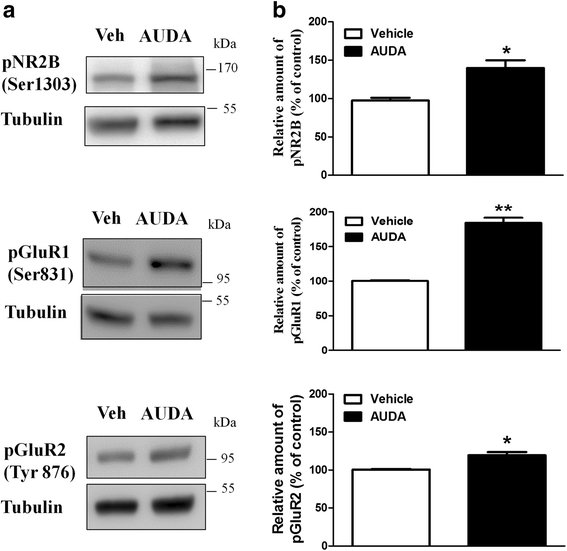
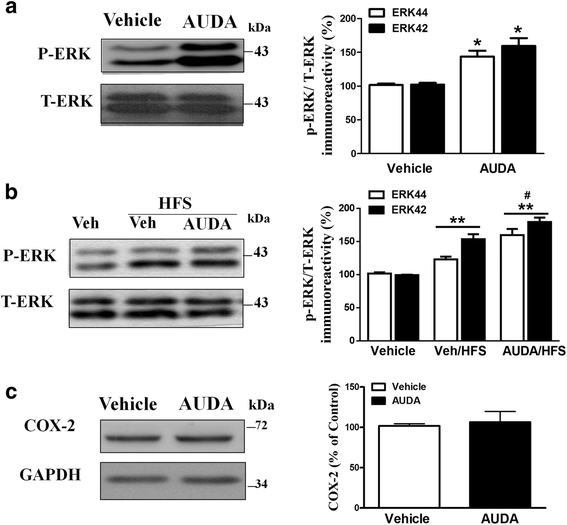
Results: Application of the sEH C-terminal epoxide hydrolase inhibitor, AUDA significantly increased the amplitude of mEPSCs and fEPSPs in prefrontal cortex neurons, while additionally enhancing long term potentiation (LTP). Western Blotting demonstrated that AUDA treatment increased the expression of the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor (NMDA) subunits NR1, NR2A, NR2B; the α-Amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid (AMPA) receptor subunits GluR1, GluR2, and ERK phosphorylation.
Conclusions: Inhibition of sEH induced an enhancement of PFC neuronal synaptic neurotransmission. This enhancement of synaptic neurotransmission is associated with an enhanced postsynaptic glutamatergic receptor and postsynaptic glutamatergic receptor mediated synaptic LTP. LTP is enhanced via ERK phosphorylation resulting from the delivery of glutamate receptors into the PFC by post-synapse by treatment with AUDA. These findings provide a possible link between synaptic function and memory processes.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Blockade of soluble epoxide hydrolase attenuates post-ischemic neuronal hyperexcitation and confers resilience against stroke with TrkB activation.Sci Rep. 2018 Jan 8;8(1):118. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-18558-6. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29311641 Free PMC article.
-
Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase Inhibition Attenuates Excitotoxicity Involving 14,15-Epoxyeicosatrienoic Acid-Mediated Astrocytic Survival and Plasticity to Preserve Glutamate Homeostasis.Mol Neurobiol. 2019 Dec;56(12):8451-8474. doi: 10.1007/s12035-019-01669-8. Epub 2019 Jul 1. Mol Neurobiol. 2019. PMID: 31257558
-
Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase Inhibitor and 14,15-Epoxyeicosatrienoic Acid-Facilitated Long-Term Potentiation through cAMP and CaMKII in the Hippocampus.Neural Plast. 2017;2017:3467805. doi: 10.1155/2017/3467805. Epub 2017 Aug 24. Neural Plast. 2017. PMID: 29138698 Free PMC article.
-
Soluble epoxide hydrolase: a new target for cardioprotection.Curr Opin Investig Drugs. 2009 Mar;10(3):253-8. Curr Opin Investig Drugs. 2009. PMID: 19333883 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Contribution of NMDA receptors to dorsolateral prefrontal cortical networks in primates.Neurosci Bull. 2015 Apr;31(2):191-7. doi: 10.1007/s12264-014-1504-6. Epub 2015 Mar 9. Neurosci Bull. 2015. PMID: 25754145 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Blockade of soluble epoxide hydrolase attenuates post-ischemic neuronal hyperexcitation and confers resilience against stroke with TrkB activation.Sci Rep. 2018 Jan 8;8(1):118. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-18558-6. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29311641 Free PMC article.
-
Cytochrome P450 derived epoxidized fatty acids as a therapeutic tool against neuroinflammatory diseases.Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2020 Apr;147:106385. doi: 10.1016/j.prostaglandins.2019.106385. Epub 2019 Nov 5. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2020. PMID: 31698143 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Soluble epoxide hydrolase as a therapeutic target for pain, inflammatory and neurodegenerative diseases.Pharmacol Ther. 2017 Dec;180:62-76. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2017.06.006. Epub 2017 Jun 19. Pharmacol Ther. 2017. PMID: 28642117 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase and Brain Cholesterol Metabolism.Front Mol Neurosci. 2020 Jan 29;12:325. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2019.00325. eCollection 2019. Front Mol Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32063836 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sex-Specific Response of the Brain Free Oxylipin Profile to Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase Inhibition.Nutrients. 2023 Feb 28;15(5):1214. doi: 10.3390/nu15051214. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 36904213 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

