Observer variability of absolute and relative thrombus density measurements in patients with acute ischemic stroke
- PMID: 26494462
- PMCID: PMC4773501
- DOI: 10.1007/s00234-015-1607-4
Observer variability of absolute and relative thrombus density measurements in patients with acute ischemic stroke
Abstract
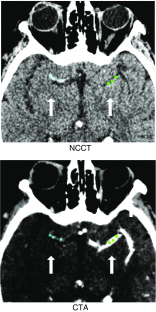
Introduction: Thrombus density may be a predictor for acute ischemic stroke treatment success. However, only limited data on observer variability for thrombus density measurements exist. This study assesses the variability and bias of four common thrombus density measurement methods by expert and non-expert observers.
Methods: For 132 consecutive patients with acute ischemic stroke, three experts and two trained observers determined thrombus density by placing three standardized regions of interest (ROIs) in the thrombus and corresponding contralateral arterial segment. Subsequently, absolute and relative thrombus densities were determined using either one or three ROIs. Intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC) was determined, and Bland-Altman analysis was performed to evaluate interobserver and intermethod agreement. Accuracy of the trained observer was evaluated with a reference expert observer using the same statistical analysis.
Results: The highest interobserver agreement was obtained for absolute thrombus measurements using three ROIs (ICCs ranging from 0.54 to 0.91). In general, interobserver agreement was lower for relative measurements, and for using one instead of three ROIs. Interobserver agreement of trained non-experts and experts was similar. Accuracy of the trained observer measurements was comparable to the expert interobserver agreement and was better for absolute measurements and with three ROIs. The agreement between the one ROI and three ROI methods was good.
Conclusion: Absolute thrombus density measurement has superior interobserver agreement compared to relative density measurement. Interobserver variation is smaller when multiple ROIs are used. Trained non-expert observers can accurately and reproducibly assess absolute thrombus densities using three ROIs.
Keywords: Brain ischemia; Computed tomography; Observer agreements; Thromboembolism; X-ray.
Figures
References
-
- Wintermark M, Sanelli PC, Albers GW, et al. Imaging recommendations for acute stroke and transient ischemic attack patients: a joint statement by the American Society of Neuroradiology, the American College of Radiology and the Society of NeuroInterventional Surgery. J Am Coll Radiol. 2013;10:828–32. doi: 10.1016/j.jacr.2013.06.019. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical