DNA damage-induced ephrin-B2 reverse signaling promotes chemoresistance and drives EMT in colorectal carcinoma harboring mutant p53
- PMID: 26494468
- PMCID: PMC4986638
- DOI: 10.1038/cdd.2015.133
DNA damage-induced ephrin-B2 reverse signaling promotes chemoresistance and drives EMT in colorectal carcinoma harboring mutant p53
Abstract
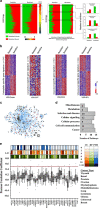
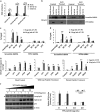
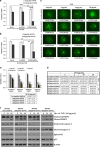
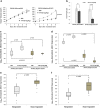
Mutation in the TP53 gene positively correlates with increased incidence of chemoresistance in different cancers. In this study, we investigated the mechanism of chemoresistance and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in colorectal cancer involving the gain-of-function (GOF) mutant p53/ephrin-B2 signaling axis. Bioinformatic analysis of the NCI-60 data set and subsequent hub prediction identified EFNB2 as a possible GOF mutant p53 target gene, responsible for chemoresistance. We show that the mutant p53-NF-Y complex transcriptionally upregulates EFNB2 expression in response to DNA damage. Moreover, the acetylated form of mutant p53 protein is recruited on the EFNB2 promoter and positively regulates its expression in conjunction with coactivator p300. In vitro cell line and in vivo nude mice data show that EFNB2 silencing restores chemosensitivity in mutant p53-harboring tumors. In addition, we observed high expression of EFNB2 in patients having neoadjuvant non-responder colorectal carcinoma compared with those having responder version of the disease. In the course of deciphering the drug resistance mechanism, we also show that ephrin-B2 reverse signaling induces ABCG2 expression after drug treatment that involves JNK-c-Jun signaling in mutant p53 cells. Moreover, 5-fluorouracil-induced ephrin-B2 reverse signaling promotes tumorigenesis through the Src-ERK pathway, and drives EMT via the Src-FAK pathway. We thus conclude that targeting ephrin-B2 might enhance the therapeutic potential of DNA-damaging chemotherapeutic agents in mutant p53-bearing human tumors.
Figures



References
-
- Cayuso J, Xu Q, Wilkinson DG. Mechanisms of boundary formation by Eph receptor and ephrin signaling. Dev Biol 2015; 401: 122–131. - PubMed
-
- Tallquist MD, Soriano P, Klinghoffer RA. Growth factor signaling pathways in vascular development. Oncogene 1999; 18: 7917–7932. - PubMed
-
- Pasquale EB. Eph receptor signalling casts a wide net on cell behaviour. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2005; 6: 462–475. - PubMed
-
- Senturk A, Pfennig S, Weiss A, Burk K, Acker-Palmer A. Ephrin Bs are essential components of the Reelin pathway to regulate neuronal migration. Nature 2011; 472: 356–360. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

