AnABlast: a new in silico strategy for the genome-wide search of novel genes and fossil regions
- PMID: 26494834
- PMCID: PMC4675712
- DOI: 10.1093/dnares/dsv025
AnABlast: a new in silico strategy for the genome-wide search of novel genes and fossil regions
Abstract
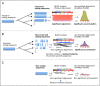
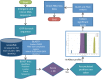
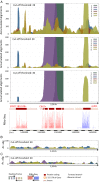
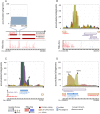
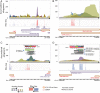
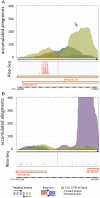
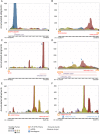
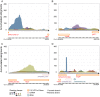
Genome annotation, assisted by computer programs, is one of the great advances in modern biology. Nevertheless, the in silico identification of small and complex coding sequences is still challenging. We observed that amino acid sequences inferred from coding-but rarely from non-coding-DNA sequences accumulated alignments in low-stringency BLAST searches, suggesting that this alignments accumulation could be used to highlight coding regions in sequenced DNA. To investigate this possibility, we developed a computer program (AnABlast) that generates profiles of accumulated alignments in query amino acid sequences using a low-stringency BLAST strategy. To validate this approach, all six-frame translations of DNA sequences between every two annotated exons of the fission yeast genome were analysed with AnABlast. AnABlast-generated profiles identified three new copies of known genes, and four new genes supported by experimental evidence. New pseudogenes, ancestral carboxyl- and amino-terminal subtractions, complex gene rearrangements, and ancient fragments of mitDNA and of bacterial origin, were also inferred. Thus, this novel in silico approach provides a powerful tool to uncover new genes, as well as fossil-coding sequences, thus providing insight into the evolutionary history of annotated genomes.
Keywords: Schizosaccharomyces pombe; fossil DNA sequences; genome evolution; in silico annotation tool; new genes.
© The Author 2015. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Kazusa DNA Research Institute.
Figures
Similar articles
-
AnABlast: Re-searching for Protein-Coding Sequences in Genomic Regions.Methods Mol Biol. 2019;1962:207-214. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-9173-0_12. Methods Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 31020562
-
Ancient evolutionary signals of protein-coding sequences allow the discovery of new genes in the Drosophila melanogaster genome.BMC Genomics. 2020 Mar 5;21(1):210. doi: 10.1186/s12864-020-6632-y. BMC Genomics. 2020. PMID: 32138644 Free PMC article.
-
[Analysis, identification and correction of some errors of model refseqs appeared in NCBI Human Gene Database by in silico cloning and experimental verification of novel human genes].Yi Chuan Xue Bao. 2004 May;31(5):431-43. Yi Chuan Xue Bao. 2004. PMID: 15478601 Chinese.
-
Comparative genomics of yeast species: new insights into their biology.Int Microbiol. 2003 Sep;6(3):183-90. doi: 10.1007/s10123-003-0132-1. Epub 2003 Jul 29. Int Microbiol. 2003. PMID: 12898398 Review.
-
PomBase: The Scientific Resource for Fission Yeast.Methods Mol Biol. 2018;1757:49-68. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-7737-6_4. Methods Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 29761456 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Using AnABlast for intergenic sORF prediction in the Caenorhabditis elegans genome.Bioinformatics. 2020 Dec 8;36(19):4827-4832. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btaa608. Bioinformatics. 2020. PMID: 32614398 Free PMC article.
-
CRISPR sequences are sometimes erroneously translated and can contaminate public databases with spurious proteins containing spaced repeats.Database (Oxford). 2020 Jan 1;2020:baaa088. doi: 10.1093/database/baaa088. Database (Oxford). 2020. PMID: 33206958 Free PMC article.
-
Computational Methods for Pseudogene Annotation Based on Sequence Homology.Methods Mol Biol. 2021;2324:35-48. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-1503-4_3. Methods Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 34165707 Review.
-
Proteomic analysis of meiosis and characterization of novel short open reading frames in the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe.Cell Cycle. 2020 Jul;19(14):1777-1785. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2020.1779470. Epub 2020 Jun 17. Cell Cycle. 2020. PMID: 32594847 Free PMC article.
-
Translation and natural selection of micropeptides from long non-canonical RNAs.Nat Commun. 2022 Oct 31;13(1):6515. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-34094-y. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 36316320 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhang M.Q. 2002, Computational prediction of eukaryotic protein-coding genes, Nat. Rev. Genet., 3, 698–709. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

