Strong Constraint on Human Genes Escaping X-Inactivation Is Modulated by their Expression Level and Breadth in Both Sexes
- PMID: 26494842
- PMCID: PMC4751236
- DOI: 10.1093/molbev/msv225
Strong Constraint on Human Genes Escaping X-Inactivation Is Modulated by their Expression Level and Breadth in Both Sexes
Abstract
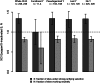
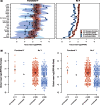
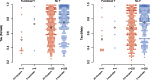
In eutherian mammals, X-linked gene expression is normalized between XX females and XY males through the process of X chromosome inactivation (XCI). XCI results in silencing of transcription from one ChrX homolog per female cell. However, approximately 25% of human ChrX genes escape XCI to some extent and exhibit biallelic expression in females. The evolutionary basis of this phenomenon is not entirely clear, but high sequence conservation of XCI escapers suggests that purifying selection may directly or indirectly drive XCI escape at these loci. One hypothesis is that this signal results from contributions to developmental and physiological sex differences, but presently there is limited evidence supporting this model in humans. Another potential driver of this signal is selection for high and/or broad gene expression in both sexes, which are strong predictors of reduced nucleotide substitution rates in mammalian genes. Here, we compared purifying selection and gene expression patterns of human XCI escapers with those of X-inactivated genes in both sexes. When we accounted for the functional status of each ChrX gene's Y-linked homolog (or "gametolog"), we observed that XCI escapers exhibit greater degrees of purifying selection in the human lineage than X-inactivated genes, as well as higher and broader gene expression than X-inactivated genes across tissues in both sexes. These results highlight a significant role for gene expression in both sexes in driving purifying selection on XCI escapers, and emphasize these genes' potential importance in human disease.
© The Author 2015. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Society for Molecular Biology and Evolution.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Strong purifying selection at genes escaping X chromosome inactivation.Mol Biol Evol. 2010 Nov;27(11):2446-50. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msq143. Epub 2010 Jun 9. Mol Biol Evol. 2010. PMID: 20534706 Free PMC article.
-
Cross-species examination of X-chromosome inactivation highlights domains of escape from silencing.Epigenetics Chromatin. 2021 Feb 17;14(1):12. doi: 10.1186/s13072-021-00386-8. Epigenetics Chromatin. 2021. PMID: 33597016 Free PMC article.
-
Landscape of X chromosome inactivation across human tissues.Nature. 2017 Oct 11;550(7675):244-248. doi: 10.1038/nature24265. Nature. 2017. PMID: 29022598 Free PMC article.
-
Genes that escape from X-chromosome inactivation: Potential contributors to Klinefelter syndrome.Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet. 2020 Jun;184(2):226-238. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.c.31800. Epub 2020 May 22. Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet. 2020. PMID: 32441398 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Escape From X-Chromosome Inactivation: An Evolutionary Perspective.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2019 Oct 22;7:241. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2019.00241. eCollection 2019. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2019. PMID: 31696116 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
When the Lyon(ized chromosome) roars: ongoing expression from an inactive X chromosome.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2017 Nov 5;372(1733):20160355. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2016.0355. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28947654 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of X-chromosome Tenomodulin Genetic Variants on Obesity in a Children's Cohort and Implications of the Gene in Adipocyte Metabolism.Sci Rep. 2019 Mar 8;9(1):3979. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-40482-0. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30850679 Free PMC article.
-
Dosage compensation of the sex chromosomes and autosomes.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2016 Aug;56:9-18. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2016.04.013. Epub 2016 Apr 22. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2016. PMID: 27112542 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New Advances in Human X chromosome status from a Developmental and Stem Cell Biology.Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2017 Dec;14(6):643-652. doi: 10.1007/s13770-017-0096-4. Epub 2017 Nov 22. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2017. PMID: 29276809 Free PMC article.
-
Leveraging sex-genetic interactions to understand brain disorders: recent advances and current gaps.Brain Commun. 2024 Jun 3;6(3):fcae192. doi: 10.1093/braincomms/fcae192. eCollection 2024. Brain Commun. 2024. PMID: 38894947 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bione S, Sala C, Manzini C, Arrigo G, Zuffardi O, Banfi S, Borsani G, Jonveaux P, Philippe C, Zuccotti M, et al. 1998. A human homologue of the Drosophila melanogaster diaphanous gene is disrupted in a patient with premature ovarian failure: evidence for conserved function in oogenesis and implications for human sterility. Am J Hum Genet. 62:533–541. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Brown CJ, Greally JM. 2003. A stain upon the silence: genes escaping X inactivation. Trends Genet. 19:432–438. - PubMed
-
- Carrel L, Willard HF. 2005. X-inactivation profile reveals extensive variability in X-linked gene expression in females. Nature 434:400–404. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

