Large nuclear vacuoles in spermatozoa negatively affect pregnancy rate in IVF cycles
- PMID: 26494990
- PMCID: PMC4609322
Large nuclear vacuoles in spermatozoa negatively affect pregnancy rate in IVF cycles
Abstract
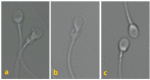
Background: Recently, motile sperm organelle morphology examination (MSOME) criteria as a new real time tool for evaluation of spermatozoa in intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) cycles has been considered.
Objective: The aim was to investigate the predictive value of MSOME in in vitro fertilization (IVF) in comparison to ICSI cycles and evaluation of the association between MSOME parameters and traditional sperm parameters in both groups.
Materials and methods: This is a cross sectional prospective analysis of MSOME parameters in IVF (n=31) and ICSI cycles (n=35). MSOME parameters were also evaluated as the presence of vacuole (none, small, medium, large or mix); head size (normal, small or large); cytoplasmic droplet; head shape and acrosome normality. In sub-analysis, MSOME parameters were compared between two groups with successful or failed clinical pregnancy in each group.
Results: In IVF group, the rate of large nuclear vacuole showed significant increase in failed as compared to successful pregnancies (13.81±9.7vs7.38±4.4, respectively, p=0.045) while MSOME parameters were the same between successful and failed pregnancies in ICSI group. Moreover, a negative correlation was noticed between LNV and sperm shape normalcy. In ICSI group, a negative correlation was established between cytoplasmic droplet and sperm shape normalcy. In addition, there was a positive correlation between sperm shape normalcy and non-vacuolated spermatozoa.
Conclusion: The high rate of large nuclear vacuoles in sperm used in IVF cycles with failed pregnancies confirms that MSOME, is a helpful tool for fine sperm morphology assessment, and its application may enhance the assisted reproduction technology success rates.
Keywords: ICSI; IVF; MSOME; Pregnancy rate; Sperm head vacuole.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Predicting the clinical outcome of ICSI by sperm head vacuole examination.Syst Biol Reprod Med. 2017 Feb;63(1):29-36. doi: 10.1080/19396368.2016.1261203. Epub 2016 Dec 23. Syst Biol Reprod Med. 2017. PMID: 28010131
-
Motile sperm organelle morphology examination (MSOME) can predict outcomes of conventional in vitro fertilization: A prospective pilot diagnostic study.Hum Fertil (Camb). 2015;18(4):258-64. doi: 10.3109/14647273.2015.1072645. Hum Fertil (Camb). 2015. PMID: 26646391
-
Motile sperm organelle morphology examination (MSOME): intervariation study of normal sperm and sperm with large nuclear vacuoles.Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2010 Jun 7;8:56. doi: 10.1186/1477-7827-8-56. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2010. PMID: 20529256 Free PMC article.
-
Observation of spermatozoa by a high-magnification microscope.Reprod Med Biol. 2013 Jul 20;13(1):21-28. doi: 10.1007/s12522-013-0164-y. eCollection 2014 Jan. Reprod Med Biol. 2013. PMID: 29662368 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Twelve years of MSOME and IMSI: a review.Reprod Biomed Online. 2013 Oct;27(4):338-52. doi: 10.1016/j.rbmo.2013.06.011. Epub 2013 Jun 28. Reprod Biomed Online. 2013. PMID: 23948449 Review.
Cited by
-
Association between early embryo morphokinetics plus transcript levels of sperm apoptotic genes and clinical outcomes in IMSI and ICSI cycles of male factor patients.J Assist Reprod Genet. 2020 Oct;37(10):2555-2567. doi: 10.1007/s10815-020-01910-7. Epub 2020 Aug 7. J Assist Reprod Genet. 2020. PMID: 32767204 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The Beneficial Role of Intra Cytoplasmic Morphologically Selected Sperm Injection (IMSI) in Assisted Reproduction.J Reprod Infertil. 2020 Jan-Mar;21(1):3-10. J Reprod Infertil. 2020. PMID: 32175260 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vitrification Increased Vacuolization of Human Spematozoa: Application of MSOME Technology.J Reprod Infertil. 2017 Apr-Jun;18(2):225-230. J Reprod Infertil. 2017. PMID: 28868247 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Palermo G, Joris H, Devroey P, Van Steirteghem AC. Pregnancies after intracytoplasmic injection of single spermatozoon into an oocyte. Lancet. 1992;340:17–18. - PubMed
-
- Cassuto NG, Bouret D, Plouchart JM, Jellad S, Vanderzwalmen P, Balet R, et al. A new real-time morphology classification for human spermatozoa: a link for fertilization and improved embryo quality. Fertil Steril. 2009;92:1616–1625. - PubMed
-
- Bonde JPE, Ernst E, Jensen TK, Hjollund NHI, Kolstad H, Scheike T, et al. Relation between semen quality and fertility: a population-based study of 430 first-pregnancy planners. Lancet. 1998;352:1172–1177. - PubMed
-
- Van Waart J, Kruger T, Lombard C, Ombelet W. Predictive value of normal sperm morphology in intrauterine insemination (IUI): a structured literature review. Hum Reprod Update. 2001;7:495–500. - PubMed
-
- Kruger TF, Menkveld R, Stander F, Lombard C, Van der Merwe J, Van Zyl J, et al. Sperm morphologic features as a prognostic factor in in vitro fertilization. Fertil Steril. 1986;46:1118–1123. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
