Bile Acid Determination after Standardized Glucose Load in Pregnant Women
- PMID: 26495178
- PMCID: PMC4603848
- DOI: 10.1055/s-0035-1555128
Bile Acid Determination after Standardized Glucose Load in Pregnant Women
Abstract
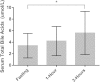
Objective Intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy (ICP) is a rare liver disorder, usually manifesting in the third trimester and associated with increased perinatal morbidity and mortality. The hallmark laboratory abnormality in ICP is elevated fasting serum bile acids; however, there are limited data on whether a nonfasting state affects a pregnant woman's total bile acids. This study assesses fasting and nonfasting bile acid levels in 10 healthy pregnant women after a standardized glucose load to provide insight into the effects of a glucose load on bile acid profiles. Study Design Pilot prospective cohort analysis of serum bile acids in pregnant women. A total of 10 healthy pregnant women from 28 to 32 weeks' gestation were recruited for the study before undergoing a glucose tolerance test. Total serum bile acids were collected for each subject in the overnight fasting state, and 1 and 3 hours after the 100-g glucose load. Results There was a statistically significant difference between fasting versus 3-hour values. There was no statistically significant difference between fasting versus 1-hour and 1-hour versus 3-hour values. Conclusion There is a difference between fasting and nonfasting total serum bile acids after a 100-g glucose load in healthy pregnant women.
Keywords: bile acids; cholestasis; liver disease; pregnancy.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect of Fasting on Total Bile Acid Levels in Pregnancy.Obstet Gynecol. 2020 Dec;136(6):1204-1210. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000004160. Obstet Gynecol. 2020. PMID: 33156200
-
The concentrations of bile acids and erythropoietin in pregnant women with intrahepatic cholestasis and the state of the fetus and newborn.Med Wieku Rozwoj. 2013 Jul-Sep;17(3):232-45. Med Wieku Rozwoj. 2013. PMID: 24296447
-
[Clinical practice guidelines of the Team of Experts of the Polish Gynecological Society: management of the intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy].Ginekol Pol. 2012 Sep;83(9):713-7. Ginekol Pol. 2012. PMID: 23342903 Polish.
-
Intrahepatic Cholestasis in Pregnancy: Review of the Literature.J Clin Med. 2020 May 6;9(5):1361. doi: 10.3390/jcm9051361. J Clin Med. 2020. PMID: 32384779 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy: changes in maternal-fetal bile acid balance and improvement by ursodeoxycholic acid.Ann Hepatol. 2002 Jan-Mar;1(1):20-8. Ann Hepatol. 2002. PMID: 15114292 Review.
Cited by
-
Intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy.Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2025 Jul 24;11(1):51. doi: 10.1038/s41572-025-00633-2. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2025. PMID: 40707479 Review.
-
Intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy - Time to redefine the reference range of total serum bile acids: A cross-sectional study.BJOG. 2022 Oct;129(11):1887-1896. doi: 10.1111/1471-0528.17174. Epub 2022 Apr 22. BJOG. 2022. PMID: 35373886 Free PMC article.
-
[Intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy].Gynakologe. 2021;54(5):341-356. doi: 10.1007/s00129-021-04787-4. Epub 2021 Apr 20. Gynakologe. 2021. PMID: 33896963 Free PMC article. German.
-
Management of Intrahepatic Cholestasis of Pregnancy: Recommendations of the Working Group on Obstetrics and Prenatal Medicine - Section on Maternal Disorders.Geburtshilfe Frauenheilkd. 2021 Aug;81(8):922-939. doi: 10.1055/a-1386-3912. Epub 2021 Aug 9. Geburtshilfe Frauenheilkd. 2021. PMID: 34393256 Free PMC article.
-
Bile Acids in Intrahepatic Cholestasis of Pregnancy.Diagnostics (Basel). 2022 Nov 9;12(11):2746. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12112746. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36359589 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Pathak B, Sheibani L, Lee R H. Cholestasis of pregnancy. Obstet Gynecol Clin North Am. 2010;37(2):269–282. - PubMed
-
- Yoong W, Memtsa M, Pun S, West P, Loo C, Okolo S. Pregnancy outcomes of women with pruritus, normal bile salts and liver enzymes: a case control study. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2008;87(4):419–422. - PubMed
-
- Webb G J, Elsharkawy A M, Hirschfield G M. The etiology of intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy: towards solving a monkey puzzle. Am J Gastroenterol. 2014;109(1):85–88. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources