Sonographic Optic Nerve Sheath Diameter as a Screening Tool for Detection of Elevated Intracranial Pressure
- PMID: 26495330
- PMCID: PMC4614555
Sonographic Optic Nerve Sheath Diameter as a Screening Tool for Detection of Elevated Intracranial Pressure
Abstract
Introduction: Timely diagnosis and treatment of post-traumatic elevated intracranial pressure (EICP) could be reduced morbidity and mortality, and improved patients' outcome. This study is trying to evaluate the diagnostic accuracy of sonographic optic nerve sheath diameter (ONSD) in detection of EICP.
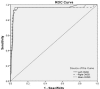
Methods: Sonographic ONSD of patients with head trauma or cerebrovascular accident suspicious for EICP were evaluated by a trained chief resident of emergency medicine, who was blind to the clinical and brain computed tomography scan (BCT) findings of patients. Immediately after ultrasonography, BCT was performed and reported by an expert radiologist without awareness from other results of the patients. Finally, ultrasonographic and BCT findings regarding EICP were compared. To evaluate the ability of sonographic ONSD in predicting the BCT findings and obtain best cut-off level, receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve were used. Sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value (PPV), negative predictive value (NPV), positive likelihood ratio (PLR), and negative likelihood ratio (NLR) of sonographic ONSD in determining of EICP was calculated. P < 0.05 was considered as statistically significant.
Results: There were 222 patients (65.3% male), with mean age of 42.2±19.5 years (range: 16-90 years). BCT showed signs of EICP, in 28 cases (12.6%). The means of the ONSD in the patients with EICP and normal ICP were 5.5 ± 0.56 and 3.93 ± 0.53 mm, respectively (P<0.0001). ROC curve demonstrated that the best cut off was 4.85 mm. Sensitivity, specificity, PPV, NPV, PLR, and NLR of ONSD for prediction of EICP were 96.4%, 95.3%, 72.2%, 98.9%, 20.6, and 0.04, respectively.
Conclusion: Sonographic diameter of optic nerve sheath could be considered as an available, accurate, and noninvasive screening tool in determining the elevated intracranial pressure in cases with head trauma or cerebrovascular accident.
Keywords: Intracranial pressure; optic nerve; tomography; traumatic brain injury; ultrasonography.
Figures
References
-
- Montazeri A. Road-traffic-related mortality in Iran: a descriptive study. Public Health. 2004;118(2):110–3. - PubMed
-
- Vahedi K, Hofmeijer J, Juettler E, et al. Early decompressive surgery in malignant infarction of the middle cerebral artery: a pooled analysis of three randomised controlled trials. The Lancet Neurology. 2007;6(3):215–22. - PubMed
-
- Sankhyan N, Vykunta Raju KN, Sharma S, Gulati S. Management of raised intracranial pressure. Indian J Pediatr. 2010;77(12):1409–16. - PubMed
-
- Tuite GF, Chong WK, Evanson J, et al. The effectiveness of papilledema as an indicator of raised intracrani al pressure in children with craniosynostosis. Neurosurgery. 1996;38(2):272–8. - PubMed
-
- Hamilton DR, Sargsyan AE, Melton SL, et al. Sonography for determining the optic nerve sheath diameter with increasing intracranial pressure in a porcine model. J Ultrasound Med. 2011;30(5):651–9. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources