Intervertebral Disc Cells Produce Interleukins Found in Patients with Back Pain
- PMID: 26495812
- PMCID: PMC4841745
- DOI: 10.1097/PHM.0000000000000399
Intervertebral Disc Cells Produce Interleukins Found in Patients with Back Pain
Abstract
Objective: To examine the link between cytokines in intervertebral disc (IVD) tissues and axial back pain.
Design: In vitro study with human IVD cells cultured from cadaveric donors and annulus fibrosus (AF) tissues from patients.
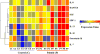
Results: Cultured nucleus pulposus (NP) and AF cells were stimulated with interleukin (IL)-1β. IL-8 and IL-7 gene expression was analyzed using real-time polymerase chain reaction. IL-8 protein was quantified by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. After IL-1β stimulation, IL-8 gene expression increased 26,541 fold in NP cells and 22,429 fold in AF cells, whereas protein released by the NP and AF cells increased 2,389- and 1,784-fold, respectively. IL-7 gene expression increased 3.3-fold in NP cells (P < 0.05).Cytokine profiles in AF tissues collected from patients undergoing surgery for back pain (painful group) or scoliosis (controls) were compared by cytokine array. IL-8 protein in the AF tissues from patients with back pain was 1.81-fold of that in controls. IL-7 and IL-10 in AF tissues from the painful group were 6.87 and 4.63 times greater than the corresponding values in controls, respectively (P < 0.05).
Conclusion: Inflammatory mediators found in AF tissues from patients with discogenic back pain are likely produced by IVD cells and may play a key role in back pain.
Figures


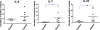
References
-
- United states bone and joint initiative: The burden of musculoskeletal diseases in the united states. 2011;2:21.
-
- DePalma MJ, Ketchum JM, Saullo T. What is the source of chronic low back pain and does age play a role? Pain Med. 2011;12:224–233. - PubMed
-
- Schwarzer AC, Aprill CN, Derby R, Fortin J, Kine G, Bogduk N. The prevalence and clinical features of internal disc disruption in patients with chronic low back pain. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1995;20:1878–1883. - PubMed
-
- Wolfer LR, Derby R, Lee JE, Lee SH. Systematic review of lumbar provocation discography in asymptomatic subjects with a meta-analysis of false-positive rates. Pain Physician. 2008;11:513–538. - PubMed
-
- Carragee EJ, Lincoln T, Parmar VS, Alamin T. A gold standard evaluation of the “discogenic pain” diagnosis as determined by provocative discography. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2006;31:2115–2123. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

