Intussusceptive-like angiogenesis in human fetal lung xenografts: Link with bronchopulmonary dysplasia-associated microvascular dysangiogenesis?
- PMID: 26495956
- PMCID: PMC4764792
- DOI: 10.3109/01902148.2015.1080321
Intussusceptive-like angiogenesis in human fetal lung xenografts: Link with bronchopulmonary dysplasia-associated microvascular dysangiogenesis?
Abstract
Background: Human fetal lung xenografts display an unusual pattern of non-sprouting, plexus-forming angiogenesis that is reminiscent of the dysmorphic angioarchitecture described in bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD). The aim of this study was to determine the clinicopathological correlates, growth characteristics and molecular regulation of this aberrant form of graft angiogenesis.
Methods: Fetal lung xenografts, derived from 12 previable fetuses (15 to 22 weeks' gestation) and engrafted in the renal subcapsular space of SCID-beige mice, were analyzed 4 weeks posttransplantation for morphology, vascularization, proliferative activity and gene expression.
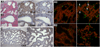
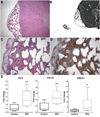
Results: Focal plexus-forming angiogenesis (PFA) was observed in 60/230 (26%) of xenografts. PFA was characterized by a complex network of tortuous nonsprouting vascular structures with low endothelial proliferative activity, suggestive of intussusceptive-type angiogenesis. There was no correlation between the occurrence of PFA and gestational age or time interval between delivery and engraftment. PFA was preferentially localized in the relatively hypoxic central subcapsular area. Microarray analysis suggested altered expression of 15 genes in graft regions with PFA, of which 7 are known angiogenic/lymphangiogenic regulators and 5 are known hypoxia-inducible genes. qRT-PCR analysis confirmed significant upregulation of SULF2, IGF2, and HMOX1 in graft regions with PFA.
Conclusion: These observations in human fetal lungs ex vivo suggest that postcanalicular lungs can switch from sprouting angiogenesis to an aberrant intussusceptive-type of angiogenesis that is highly reminiscent of BPD-associated dysangiogenesis. While circumstantial evidence suggests hypoxia may be implicated, the exact triggering mechanisms, molecular regulation and clinical implications of this angiogenic switch in preterm lungs in vivo remain to be determined.
Keywords: BPD; angiogenesis; chronic lung disease of newborn; heme oxygenase 1; insulin-like growth factor; sulfatase 2.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Stoll BJ, Hansen NI, Bell EF, Shankaran S, Laptook AR, Walsh MC, Hale EC, Newman NS, Schibler K, Carlo WA, Kennedy KA, Poindexter BB, Finer NN, Ehrenkranz RA, Duara S, Sanchez PJ, O'Shea TM, Goldberg RN, Van Meurs KP, Faix RG, Phelps DL, Frantz ID, 3rd, Watterberg KL, Saha S, Das A, Higgins RD. Neonatal outcomes of extremely preterm infants from the NICHD Neonatal Research Network. Pediatrics. 2010;126:443–456. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Vom Hove M, Prenzel F, Uhlig HH, Robel-Tillig E. Pulmonary outcome in former preterm, very low birth weight children with bronchopulmonary dysplasia: a case-control follow-up at school age. J Pediatr. 2014;164:40–45. e44. - PubMed
-
- Husain AN, Siddiqui NH, Stocker JT. Pathology of arrested acinar development in postsurfactant bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Hum Pathol. 1998;29:710–717. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
