Olfactory learning skews mushroom body output pathways to steer behavioral choice in Drosophila
- PMID: 26496148
- PMCID: PMC4835525
- DOI: 10.1016/j.conb.2015.10.002
Olfactory learning skews mushroom body output pathways to steer behavioral choice in Drosophila
Abstract
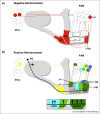
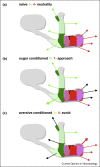
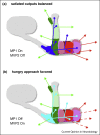
Learning permits animals to attach meaning and context to sensory stimuli. How this information is coded in neural networks in the brain, and appropriately retrieved and utilized to guide behavior, is poorly understood. In the fruit fly olfactory memories of particular value are represented within sparse populations of odor-activated Kenyon cells (KCs) in the mushroom body ensemble. During learning reinforcing dopaminergic neurons skew the mushroom body network by driving zonally restricted plasticity at synaptic junctions between the KCs and subsets of the overall small collection of mushroom body output neurons. Reactivation of this skewed KC-output neuron network retrieves memory of odor valence and guides appropriate approach or avoidance behavior.
Copyright © 2015 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Galili D.S., Dylla K.V., Ludke A., Friedrich A.B., Yamagata N., Wong J.Y., Ho C.H., Szyszka P., Tanimoto H. Converging circuits mediate temperature and shock aversive olfactory conditioning in Drosophila. Curr Biol. 2014;24:1712–1722. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

