Functional coupling between writers, erasers and readers of histone and DNA methylation
- PMID: 26496625
- PMCID: PMC4688207
- DOI: 10.1016/j.sbi.2015.09.007
Functional coupling between writers, erasers and readers of histone and DNA methylation
Abstract
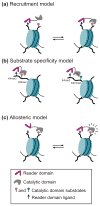
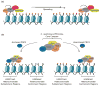
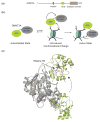
DNA and histone lysine methylation are dynamic chemical modifications that play a crucial role in the establishment of gene expression patterns during development. Both types of genomic methylation patterns are enzymatically regulated by the opposing activities of enzymes that introduce and remove these marks, known as methylation 'writers' and 'erasers', respectively. The appropriate localization and activity of these enzymes on chromatin is, in part, regulated by chromatin 'readers', protein modules that recognize histone and DNA modifications. Such reading modules are either encoded within the same polypeptide as the catalytic domains of writers and erasers, or present in protein partners that associate with them. Here, we review recent structural, biochemical and biological studies that demonstrate that there are multiple mechanisms by which reader domains can regulate the writers and erasers of histone and DNA methylation.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Strahl BD, Allis CD. The language of covalent histone modifications. Nature. 2000;403:41–45. - PubMed
-
- Jenuwein T, Allis CD. Translating the histone code. Science. 2001;293:1074–1080. - PubMed
-
- Martin C, Zhang Y. The diverse functions of histone lysine methylation. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2005;6:838–849. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

