Role of the YAP Oncoprotein in Priming Ras-Driven Rhabdomyosarcoma
- PMID: 26496700
- PMCID: PMC4619859
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0140781
Role of the YAP Oncoprotein in Priming Ras-Driven Rhabdomyosarcoma
Abstract
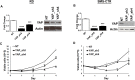
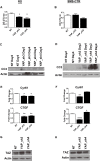
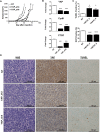
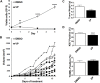
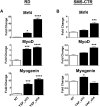
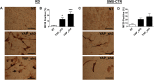
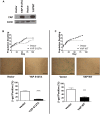
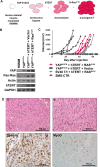
Rhabdomyosarcoma (RMS), a cancer characterized by features of skeletal muscle histogenesis, is the most common soft tissue sarcoma of childhood and adolescence. Survival for high-risk groups is less than 30% at 5 years. RMS also occurs during adulthood, with a lower incidence but higher mortality. Recently, mutational profiling has revealed a correlation between activating Ras mutations in the embryonal (eRMS) and pleomorphic (pRMS) histologic variants of RMS, and a poorer outcome for those patients. Independently, the YAP transcriptional coactivator, an oncoprotein kept in check by the Hippo tumor suppressor pathway, is upregulated in eRMS. Here we show that YAP promotes cell proliferation and antagonizes apoptosis and myogenic differentiation of human RMS cells bearing oncogenic Ras mutations in cell culture studies in vitro and in murine xenografts in vivo. Pharmacologic inhibition of YAP by the benzoporphyrin derivative verteporfin decreased cell proliferation and tumor growth in vivo. To interrogate the temporal contribution of YAP in eRMS tumorigenesis, we used a primary human cell-based genetic model of Ras-driven RMS. Constitutively active YAP functioned as an early genetic lesion, permitting bypass of senescence and priming myoblasts to tolerate subsequent expression of hTERT and oncogenic Ras, which were necessary and sufficient to generate murine xenograft tumors mimicking RMS in vivo. This work provides evidence for cooperation between YAP and oncogenic Ras in RMS tumorigenesis, laying the foundation for preclinical co-targeting of these pathways.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Hippo effector TAZ (WWTR1) transforms myoblasts and TAZ abundance is associated with reduced survival in embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma.J Pathol. 2016 Sep;240(1):3-14. doi: 10.1002/path.4745. J Pathol. 2016. PMID: 27184927 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel Notch-YAP Circuit Drives Stemness and Tumorigenesis in Embryonal Rhabdomyosarcoma.Mol Cancer Res. 2017 Dec;15(12):1777-1791. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-17-0004. Epub 2017 Sep 18. Mol Cancer Res. 2017. PMID: 28923841 Free PMC article.
-
"Verteporfin exhibits anti-proliferative activity in embryonal and alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma cell lines".Chem Biol Interact. 2019 Oct 1;312:108813. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2019.108813. Epub 2019 Sep 6. Chem Biol Interact. 2019. PMID: 31494105
-
A review and perspective paper: Ras oncogene gets modest, from kingpin to mere henchman.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024 Oct 1;81(1):412. doi: 10.1007/s00018-024-05449-z. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024. PMID: 39352544 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cutaneous mosaic RASopathies associated with rhabdomyosarcoma.Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2022 May;69(5):e29639. doi: 10.1002/pbc.29639. Epub 2022 Mar 6. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35253347 Review.
Cited by
-
YAP1 Mediates Resistance to MEK1/2 Inhibition in Neuroblastomas with Hyperactivated RAS Signaling.Cancer Res. 2019 Dec 15;79(24):6204-6214. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-19-1415. Epub 2019 Oct 31. Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 31672841 Free PMC article.
-
Functional genomics screen identifies YAP1 as a key determinant to enhance treatment sensitivity in lung cancer cells.Oncotarget. 2016 May 17;7(20):28976-88. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.6721. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26716514 Free PMC article.
-
VGLL3 operates via TEAD1, TEAD3 and TEAD4 to influence myogenesis in skeletal muscle.J Cell Sci. 2019 Jul 5;132(13):jcs225946. doi: 10.1242/jcs.225946. J Cell Sci. 2019. PMID: 31138678 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of the relationship between the KRAS G12V oncogene and the Hippo effector YAP1 in embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma.Sci Rep. 2018 Oct 23;8(1):15674. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-33852-7. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30353028 Free PMC article.
-
The Efficiency of Verteporfin as a Therapeutic Option in Pre-Clinical Models of Melanoma.J Cancer. 2019 Jan 1;10(1):1-10. doi: 10.7150/jca.27472. eCollection 2019. J Cancer. 2019. PMID: 30662519 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Stratton MR, Fisher C, Gusterson BA, Cooper CS. Detection of point mutations in N-ras and K-ras genes of human embryonal rhabdomyosarcomas using oligonucleotide probes and the polymerase chain reaction. Cancer research. 1989;49(22):6324–7. - PubMed
-
- Wilke W, Maillet M, Robinson R. H-ras-1 point mutations in soft tissue sarcomas. Modern pathology: an official journal of the United States and Canadian Academy of Pathology, Inc. 1993;6(2):129–32. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

