Morphological changes of placental syncytium and their implications for the pathogenesis of preeclampsia
- PMID: 26496726
- PMCID: PMC4846582
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-015-2069-x
Morphological changes of placental syncytium and their implications for the pathogenesis of preeclampsia
Abstract
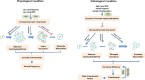
Preeclampsia is a hypertensive disease that complicates many pregnancies, typically presenting with new-onset or worsening hypertension and proteinuria. It is well recognized that the placental syncytium plays a key role in the pathogenesis of preeclampsia. This review summarizes the findings pertaining to the structural alterations in the syncytium of preeclamptic placentas and analyzes their pathological implications for the development of preeclampsia. Changes in the trophoblastic lineage, including those in the proliferation of cytotrophoblasts, the formation of syncytiotrophoblast through cell fusion, cell apoptosis and syncytial deportation, are discussed in the context of preeclampsia. Extensive correlations are made between functional deficiencies and the alterations on the levels of gross anatomy, tissue histology, cellular events, ultrastructure, molecular pathways, and gene expression. Attention is given to the significance of dynamic changes in the syncytial turnover in preeclamptic placentas. Specifically, experimental evidences for the complex and obligatory role of syncytin-1 in cell fusion, cell-cycle regulation at the G1/S transition, and apoptosis through AIF-mediated pathway, are discussed in detail in the context of syncytium homeostasis. Finally, the recent observations on the aberrant fibrin deposition in the trophoblastic layer and the trophoblast immature phenotype in preeclamptic placentas and their potential pathogenic impact are also reviewed.
Keywords: HERV-W; Nonfusogenic; Preeclampsia; Pregnancy hypertension; Syncytium.
Figures
References
-
- Hypertension in Pregnancy (2013) Task force on hypertension in pregnancy. American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. http://www.acog.org/-/media/Task-Force-and-Work-Group-Reports/Hypertensi.... Accessed Jan 2015
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

