MAP3K1 function is essential for cytoarchitecture of the mouse organ of Corti and survival of auditory hair cells
- PMID: 26496772
- PMCID: PMC4728323
- DOI: 10.1242/dmm.023077
MAP3K1 function is essential for cytoarchitecture of the mouse organ of Corti and survival of auditory hair cells
Abstract
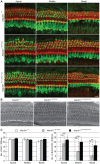
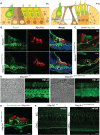
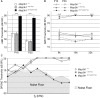
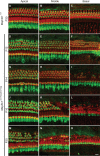
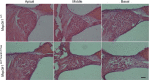
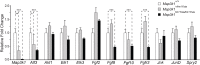
MAP3K1 is a serine/threonine kinase that is activated by a diverse set of stimuli and exerts its effect through various downstream effecter molecules, including JNK, ERK1/2 and p38. In humans, mutant alleles of MAP3K1 are associated with 46,XY sex reversal. Until recently, the only phenotype observed in Map3k1(tm1Yxia) mutant mice was open eyelids at birth. Here, we report that homozygous Map3k1(tm1Yxia) mice have early-onset profound hearing loss accompanied by the progressive degeneration of cochlear outer hair cells. In the mouse inner ear, MAP3K1 has punctate localization at the apical surface of the supporting cells in close proximity to basal bodies. Although the cytoarchitecture, neuronal wiring and synaptic junctions in the organ of Corti are grossly preserved, Map3k1(tm1Yxia) mutant mice have supernumerary functional outer hair cells (OHCs) and Deiters' cells. Loss of MAP3K1 function resulted in the downregulation of Fgfr3, Fgf8, Fgf10 and Atf3 expression in the inner ear. Fgfr3, Fgf8 and Fgf10 have a role in induction of the otic placode or in otic epithelium development in mice, and their functional deficits cause defects in cochlear morphogenesis and hearing loss. Our studies suggest that MAP3K1 has an essential role in the regulation of these key cochlear morphogenesis genes. Collectively, our data highlight the crucial role of MAP3K1 in the development and function of the mouse inner ear and hearing.
Keywords: FGF signaling pathway; Fgf10; Fgf8; Fgfr3; Hearing loss; MAPK pathway; Map3k1; Mekk1; Supernumerary outer hair cells.
© 2015. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing or financial interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The goya mouse mutant reveals distinct newly identified roles for MAP3K1 in the development and survival of cochlear sensory hair cells.Dis Model Mech. 2015 Dec;8(12):1555-68. doi: 10.1242/dmm.023176. Epub 2015 Nov 5. Dis Model Mech. 2015. PMID: 26542706 Free PMC article.
-
Deterioration of the Medial Olivocochlear Efferent System Accelerates Age-Related Hearing Loss in Pax2-Isl1 Transgenic Mice.Mol Neurobiol. 2016 May;53(4):2368-83. doi: 10.1007/s12035-015-9215-1. Epub 2015 May 20. Mol Neurobiol. 2016. PMID: 25990412
-
Hedgehog signaling regulates prosensory cell properties during the basal-to-apical wave of hair cell differentiation in the mammalian cochlea.Development. 2013 Sep;140(18):3848-57. doi: 10.1242/dev.095398. Epub 2013 Aug 14. Development. 2013. PMID: 23946445
-
Signaling regulating inner ear development: cell fate determination, patterning, morphogenesis, and defects.Congenit Anom (Kyoto). 2015 Feb;55(1):17-25. doi: 10.1111/cga.12072. Congenit Anom (Kyoto). 2015. PMID: 25040109 Review.
-
Embryonic Origins of Virus-Induced Hearing Loss: Overview of Molecular Etiology.Viruses. 2021 Jan 6;13(1):71. doi: 10.3390/v13010071. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 33419104 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Hearing impairment locus heterogeneity and identification of PLS1 as a new autosomal dominant gene in Hungarian Roma.Eur J Hum Genet. 2019 Jun;27(6):869-878. doi: 10.1038/s41431-019-0372-y. Epub 2019 Mar 14. Eur J Hum Genet. 2019. PMID: 30872814 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The hair cell analysis toolbox is a precise and fully automated pipeline for whole cochlea hair cell quantification.PLoS Biol. 2023 Mar 22;21(3):e3002041. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3002041. eCollection 2023 Mar. PLoS Biol. 2023. PMID: 36947567 Free PMC article.
-
DLK/JNK3 Upregulation Aggravates Hair Cell Senescence in Mice Cochleae via Excessive Autophagy.Aging Cell. 2025 Aug;24(8):e70099. doi: 10.1111/acel.70099. Epub 2025 May 12. Aging Cell. 2025. PMID: 40356329 Free PMC article.
-
Six1 is essential for differentiation and patterning of the mammalian auditory sensory epithelium.PLoS Genet. 2017 Sep 11;13(9):e1006967. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1006967. eCollection 2017 Sep. PLoS Genet. 2017. PMID: 28892484 Free PMC article.
-
Novel kinase regulators of extracellular matrix internalisation identified by high-content screening modulate invasive carcinoma cell migration.PLoS Biol. 2024 Dec 12;22(12):e3002930. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3002930. eCollection 2024 Dec. PLoS Biol. 2024. PMID: 39666682 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bonvin C., Guillon A., van Bemmelen M. X., Gerwins P., Johnson G. L. and Widmann C. (2002). Role of the amino-terminal domains of MEKKs in the activation of NF kappa B and MAPK pathways and in the regulation of cell proliferation and apoptosis. Cell. Signal. 14, 123-131. 10.1016/S0898-6568(01)00219-4 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cuevas B. D., Abell A. N., Witowsky J. A., Yujiri T., Johnson N. L., Kesavan K., Ware M., Jones P. L., Weed S. A., DeBiasi R. L. et al. (2003). MEKK1 regulates calpain-dependent proteolysis of focal adhesion proteins for rear-end detachment of migrating fibroblasts. EMBO J. 22, 3346-3355. 10.1093/emboj/cdg322 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

