Autoregulation of topoisomerase I expression by supercoiling sensitive transcription
- PMID: 26496944
- PMCID: PMC4770202
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkv1088
Autoregulation of topoisomerase I expression by supercoiling sensitive transcription
Abstract
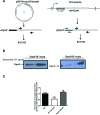
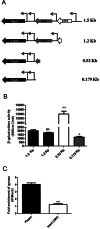
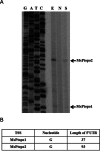
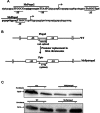
The opposing catalytic activities of topoisomerase I (TopoI/relaxase) and DNA gyrase (supercoiling enzyme) ensure homeostatic maintenance of bacterial chromosome supercoiling. Earlier studies in Escherichia coli suggested that the alteration in DNA supercoiling affects the DNA gyrase and TopoI expression. Although, the role of DNA elements around the promoters were proposed in regulation of gyrase, the molecular mechanism of supercoiling mediated control of TopoI expression is not yet understood. Here, we describe the regulation of TopoI expression from Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Mycobacterium smegmatis by a mechanism termed Supercoiling Sensitive Transcription (SST). In both the organisms, topoI promoter(s) exhibited reduced activity in response to chromosome relaxation suggesting that SST is intrinsic to topoI promoter(s). We elucidate the role of promoter architecture and high transcriptional activity of upstream genes in topoI regulation. Analysis of the promoter(s) revealed the presence of sub-optimal spacing between the -35 and -10 elements, rendering them supercoiling sensitive. Accordingly, upon chromosome relaxation, RNA polymerase occupancy was decreased on the topoI promoter region implicating the role of DNA topology in SST of topoI. We propose that negative supercoiling induced DNA twisting/writhing align the -35 and -10 elements to facilitate the optimal transcription of topoI.
© The Author(s) 2015. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures

References
-
- Champoux J.J. DNA topoisomerases: structure, function, and mechanism. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2001;70:369–413. - PubMed
-
- Wang J.C. Cellular roles of DNA topoisomerases: a molecular perspective. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2002;3:430–440. - PubMed
-
- Hatfield G.W., Benham C.J. DNA topology-mediated control of global gene expression in Escherichia coli. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2002;36:175–203. - PubMed
-
- Masse E., Drolet M. Relaxation of transcription-induced negative supercoiling is an essential function of Escherichia coli DNA topoisomerase I. J. Biol. Chem. 1999;274:16654–16658. - PubMed

