Sialylation and glycosylation modulate cell adhesion and invasion to extracellular matrix in human malignant lymphoma: Dependency on integrin and the Rho GTPase family
- PMID: 26497328
- PMCID: PMC4665765
- DOI: 10.3892/ijo.2015.3211
Sialylation and glycosylation modulate cell adhesion and invasion to extracellular matrix in human malignant lymphoma: Dependency on integrin and the Rho GTPase family
Abstract
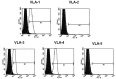
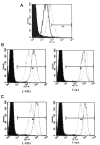
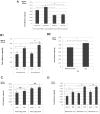
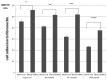
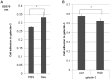
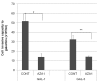
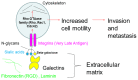
To determine the biological roles of cell surface glycosylation, we modified the surface glycosylation of human malignant lymphoma cell lines using glycosylation inhibitors. The O-glycosylation inhibitor, benzyl-α-GalNAc (BZ) enhanced the fibronectin adhesion of HBL-8 cells, a human Burkitt's lymphoma cell line, and of H-ALCL cells, a human anaplastic large cell lymphoma cell line, both of which were established in our laboratory. The N-glycosylation inhibitor, tunicamycin (TM) inhibited the surface expression of Phaseolus vulgaris leukoagglutinating (L-PHA) lectin- and Canavalia ensiformis (ConA) lectin-reactive oligosaccharides in the HBL-8 cell line. Assay of the adhesion of HBL-8 cells to fibronectin showed that fibronectin adhesion is mediated by the integrin very late antigen (VLA)-4 and that not only BZ but also TM treatment enhanced HBL-8 cell adhesion to fibronectin. Furthermore, although BZ treatment also enhanced H-ALCL cell adhesion to fibronectin, this effect was not mediated by VLA-5 or the RGD sequence of fibronectin. We also showed that H-ALCL cell adhesion to galectin-3 was enhanced by pre-treatment with neuraminidase, which cleaves cell surface sialic acid. Additionally, H-ALCL cell adhesion to galectin-3 was inhibited by pre‑treatment with the RGD peptide suggesting that cell adhesion to galectin-3 is mediated by integrin (VLA-5). Furthermore, H-ALCL cell invasion of galectin-1 and galectin-3 was inhibited by pre-treatment with the RGD peptide. Therefore, cell adhesion to and invasion of galectin-1 and galectin-3 are integrin-dependent. In addition to these findings, cell adhesion to galectin-3 was markedly inhibited by treatment with β-lactose compared to treatment with sucrose. Therefore, interactions between integrins and galectin-3 may be mediated through β-galactose that is linked to glycans of integrins. AZA1, an inhibitor of Ras homolog oncoprotein (Rho) GTPase family proteins, RAS-related C3 botulinus toxin substrate 1 (Rac 1) and Cell division control protein 42 homolog (Cdc42) markedly inhibited cell invasion of galectin-1 and galectin-3 suggesting that Rac 1 and Cdc42 may be involved in the regulation of H-ALCL cell invasion of galectins. In conclusion, artificial modification of cell surface glycosylation revealed the biological roles of glycosylation in the adhesion to and invasion of the extracellular matrix (ECM) by human malignant lymphoma cell lines. These findings will provide new insight into the glycobiology of human malignant lymphoma.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Glycosylation in lymphoma: Biology and glycotherapy.Pathol Int. 2019 Aug;69(8):441-449. doi: 10.1111/pin.12834. Epub 2019 Jul 17. Pathol Int. 2019. PMID: 31317621 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Galectin-1-mediated cell adhesion, invasion and cell death in human anaplastic large cell lymphoma: regulatory roles of cell surface glycans.Int J Oncol. 2014 May;44(5):1433-42. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2014.2319. Epub 2014 Mar 4. Int J Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24589677 Free PMC article.
-
The regulatory roles of cell surface sialylation and N-glycans in human B cell lymphoma cell adhesion to galectin-1.Int J Oncol. 2006 Jan;28(1):155-60. Int J Oncol. 2006. PMID: 16327992
-
Sialylation by β-galactoside α-2,6-sialyltransferase and N-glycans regulate cell adhesion and invasion in human anaplastic large cell lymphoma.Int J Oncol. 2015 Mar;46(3):973-80. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2015.2818. Epub 2015 Jan 7. Int J Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25573487 Free PMC article.
-
Recent progress and new perspectives in lymphoma glycobiology.Fukushima J Med Sci. 2013;59(1):1-14. doi: 10.5387/fms.59.1. Fukushima J Med Sci. 2013. PMID: 23842509 Review.
Cited by
-
Sphingolipids and Lymphomas: A Double-Edged Sword.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Apr 19;14(9):2051. doi: 10.3390/cancers14092051. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35565181 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Glycosylation in lymphoma: Biology and glycotherapy.Pathol Int. 2019 Aug;69(8):441-449. doi: 10.1111/pin.12834. Epub 2019 Jul 17. Pathol Int. 2019. PMID: 31317621 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current Methods of Post-Translational Modification Analysis and Their Applications in Blood Cancers.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Apr 16;13(8):1930. doi: 10.3390/cancers13081930. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33923680 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Altered Actin Dynamics in Cell Migration of GNE Mutant Cells.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Mar 18;9:603742. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.603742. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 33816461 Free PMC article.
-
Galectin-3 Determines Tumor Cell Adaptive Strategies in Stressed Tumor Microenvironments.Front Oncol. 2016 May 23;6:127. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2016.00127. eCollection 2016. Front Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27242966 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Suzuki O, Nozawa Y, Kawaguchi T, Abe M. Phaseolus vulgaris leukoagglutinating lectin-binding reactivity in human diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and its relevance to the patient's clinical outcome: Lectin histochemistry and lectin blot analysis. Pathol Int. 1999;49:874–880. doi: 10.1046/j.1440-1827.1999.00960.x. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Suzuki O, Nozawa Y, Kawaguchi T, Abe M. Alpha-2,6-sialylation of L-PHA reactive oligosaccharides and expression of N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase V in human diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Oncol Rep. 2003;10:1759–1764. - PubMed
-
- Suzuki O, Nozawa Y, Abe M. Loss of L-PHA-, PNA-, or ConA-reactive oligosaccharides is associated with a poor prognosis in human Burkitt's lymphoma. Oncol Rep. 2007;17:775–779. - PubMed
-
- Porowska H, Paszkiewicz-Gadek A, Anchim T, Wolczynski S, Gindzienski A. Inhibition of the O-glycan elongation limits MUC1 incorporation to cell membrane of human endometrial carcinoma cells. Int J Mol Med. 2004;13:459–464. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

