Human IgG4: a structural perspective
- PMID: 26497518
- PMCID: PMC4670484
- DOI: 10.1111/imr.12349
Human IgG4: a structural perspective
Abstract
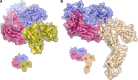
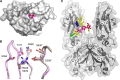
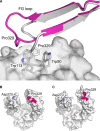
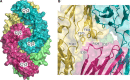
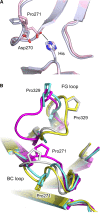
IgG4, the least represented human IgG subclass in serum, is an intriguing antibody with unique biological properties, such as the ability to undergo Fab-arm exchange and limit immune complex formation. The lack of effector functions, such as antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity and complement-dependent cytotoxicity, is desirable for therapeutic purposes. IgG4 plays a protective role in allergy by acting as a blocking antibody, and inhibiting mast cell degranulation, but a deleterious role in malignant melanoma, by impeding IgG1-mediated anti-tumor immunity. These findings highlight the importance of understanding the interaction between IgG4 and Fcγ receptors. Despite a wealth of structural information for the IgG1 subclass, including complexes with Fcγ receptors, and structures for intact antibodies, high-resolution crystal structures were not reported for IgG4-Fc until recently. Here, we highlight some of the biological properties of human IgG4, and review the recent crystal structures of IgG4-Fc. We discuss the unexpected conformations adopted by functionally important Cγ2 domain loops, and speculate about potential implications for the interaction between IgG4 and FcγRs.
Keywords: Fc receptor; IgG1; IgG4; antibody; immunoglobulin.
© 2015 The Authors. Immunological Reviews Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures

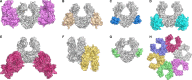
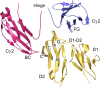


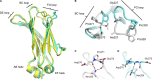


References
-
- Aalberse RC, Stapel SO, Schuurman J, Rispens T. Immunoglobulin G4: an odd antibody. Clin Exp Allergy. 2009;39:469–477. - PubMed
-
- van der Zee JS, van Swieten P, Aalberse RC. Serologic aspects of IgG4 antibodies. II. IgG4 antibodies form small, nonprecipitating immune complexes due to functional monovalency. J Immunol. 1986;137:3566–3571. - PubMed
-
- Salfeld JG. Isotype selection in antibody engineering. Nat Biotechnol. 2007;25:1369–1372. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

