FN14 and GRP94 expression are prognostic/predictive biomarkers of brain metastasis outcome that open up new therapeutic strategies
- PMID: 26497551
- PMCID: PMC4792555
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.5471
FN14 and GRP94 expression are prognostic/predictive biomarkers of brain metastasis outcome that open up new therapeutic strategies
Abstract
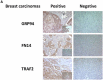
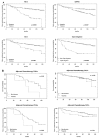
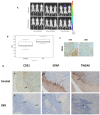
Brain metastasis is a devastating problem in patients with breast, lung and melanoma tumors. GRP94 and FN14 are predictive biomarkers over-expressed in primary breast carcinomas that metastasized in brain. To further validate these brain metastasis biomarkers, we performed a multicenter study including 318 patients with breast carcinomas. Among these patients, there were 138 patients with metastasis, of whom 84 had brain metastasis. The likelihood of developing brain metastasis increased by 5.24-fold (95%CI 2.83-9.71) and 2.55- (95%CI 1.52-4.3) in the presence of FN14 and GRP94, respectively. Moreover, FN14 was more sensitive than ErbB2 (38.27 vs. 24.68) with similar specificity (89.43 vs. 89.55) to predict brain metastasis and had identical prognostic value than triple negative patients (p < 0.0001). Furthermore, we used GRP94 and FN14 pathways and GUILD, a network-based disease-gene prioritization program, to pinpoint the genes likely to be therapeutic targets, which resulted in FN14 as the main modulator and thalidomide as the best scored drug. The treatment of mice with brain metastasis improves survival decreasing reactive astrocytes and angiogenesis, and down-regulate FN14 and its ligand TWEAK. In conclusion our results indicate that FN14 and GRP94 are prediction/prognosis markers which open up new possibilities for preventing/treating brain metastasis.
Keywords: FN14; GRP94; biomarkers; brain metastasis; breast cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
Angels Sierra has received research funding from Celgene Research, S. L.
Figures




References
-
- Tham YL, Sexton K, Kramer R, Hilsenbeck S, Elledge R. Primary breast cancer phenotypes associated with propensity for central nervous system metastases. Cancer. 2006;107:696–704. - PubMed
-
- Stemmler HJ, Heinemann V. Central nervous system metastases in HER-2-overexpressing metastatic breast cancer: a treatment challenge. Oncologist. 2008;13:739–750. - PubMed
-
- Matthias P, Capper D, Ilhan-Mutlu AI, Berghoff AS, Birner P, Bartsch R, Marosi C, Zielinski C, Mehta MP, Winkler F, Wick W, von Deimling A. Brain metastases: pathobiology and emerging targeted therapies. Acta Neuropathol. 2012;123:205–222. - PubMed
-
- Soffietti R, Trevisan E, Ruda R. Targeted therapy in brain metastasis. Curr. Opin. Oncol. 2012;24:679–686. - PubMed
-
- Lockman PR, Mittapalli RK, Taskar KS, Rudraraju V, Gril B, Bohn KA, Adkins CE, Roberts A, Thorsheim HR, Gaasch JA, Huang S, Palmieri D, Steeg PS, et al. Heterogeneous blood-tumor barrier permeability determines drug efficacy in experimental brain metastases of breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2010;16:5664–5678. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

