Upregulated in Hepatitis B virus-associated hepatocellular carcinoma cells, miR-331-3p promotes proliferation of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by targeting ING5
- PMID: 26497554
- PMCID: PMC4741986
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.5642
Upregulated in Hepatitis B virus-associated hepatocellular carcinoma cells, miR-331-3p promotes proliferation of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by targeting ING5
Abstract
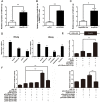
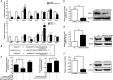
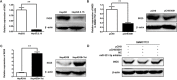
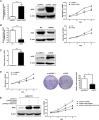
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) is a major risk factor for development and progression of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). It has been reported that viral infection can interfere with cellular microRNA (miRNA) expression and participate in the pathogenesis of oncogenicity. Our miRNAs array data indicated that miR-331-3p expression in HCC cell lines increased, but the relationship between miR-331-3p expression and HBV activity is unclear. Here, we observed elevated expression of miR-331-3p in different HCC cell lines expressing HBV. HBV, especially HBx, promotes miR-331-3p expression by enhancing its promoter activity. Using a miRNA target prediction database miRBase, we identified ING5 to be a novel target gene of miR-331-3p. miR-331-3p could inhibit ING5 expression by directly targeting its 3'-untranslated region (3'-UTR). As predicted, HBV was confirmed to repress ING5 at both mRNA and protein levels by promoting miR-331-3p expression. Our result indicated that miR-331-3p expression promotes proliferation of SMMC7721 cells by inhibiting ING5. ING5 overexpression promoted cell apoptosis in HCC cell lines. We also found ING5 expression was decreased in tumor tissue of HCC patient with HBV infection compared to its expression in para-carcinoma tissues.
Conclusion: These results showed that miR-331-3p is upregulated by HBV and promotes proliferation of HCC cells though repression of ING5 expression. These data provide new insights for understanding the mechanisms of HBV-related HCC pathogenesis.
Keywords: HBV; HCC; ING5; miR-331-3p; miRNA.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Hepatitis B virus X protein promotes proliferation of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by upregulating miR-181b by targeting ING5.Biol Chem. 2018 May 24;399(6):611-619. doi: 10.1515/hsz-2018-0178. Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 29604207
-
Role of microRNA-210-3p in hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2020 Mar 1;318(3):G401-G409. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00269.2019. Epub 2020 Jan 6. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2020. PMID: 31905024
-
miR-106b promotes cancer progression in hepatitis B virus-associated hepatocellular carcinoma.World J Gastroenterol. 2016 Jun 14;22(22):5183-92. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i22.5183. World J Gastroenterol. 2016. PMID: 27298561 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatitis B virus and microRNAs: Complex interactions affecting hepatitis B virus replication and hepatitis B virus-associated diseases.World J Gastroenterol. 2015 Jun 28;21(24):7375-99. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i24.7375. World J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 26139985 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hepatitis B virus x protein in the pathogenesis of hepatitis B virus-induced hepatocellular carcinoma.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2011 Jan;26 Suppl 1:144-52. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2010.06546.x. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2011. PMID: 21199526 Review.
Cited by
-
MicroRNA-331 inhibits development of gastric cancer through targeting musashi1.World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2019 Sep 15;11(9):705-716. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v11.i9.705. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31558975 Free PMC article.
-
The Antitumor and Sorafenib-resistant Reversal Effects of Ursolic Acid on Hepatocellular Carcinoma via Targeting ING5.Int J Biol Sci. 2024 Aug 5;20(11):4190-4208. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.97720. eCollection 2024. Int J Biol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39247819 Free PMC article.
-
The role of microRNAs in hepatocyte metabolism and hepatitis B virus replication.Virol Sin. 2016 Dec;31(6):472-479. doi: 10.1007/s12250-016-3924-0. Epub 2016 Dec 28. Virol Sin. 2016. PMID: 28063013 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The nucleocytoplasmic translocation and up-regulation of ING5 protein in breast cancer: a potential target for gene therapy.Oncotarget. 2017 May 17;8(47):81953-81966. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.17918. eCollection 2017 Oct 10. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29137236 Free PMC article.
-
Circular RNA circRASSF5 Functions as an Anti-Oncogenic Factor in Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Acting as a Competitive Endogenous RNA Through Sponging miR-331-3p.J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2022 Oct 4;9:1041-1056. doi: 10.2147/JHC.S376063. eCollection 2022. J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2022. PMID: 36217445 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yuen MF, Hou JL, Chutaputti A. Hepatocellular carcinoma in the Asia pacific region. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009;24:346–353. - PubMed
-
- Bartel D. MicroRNAs: Genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116:281–297. - PubMed
-
- Calin GA, Croce CM. MicroRNA signatures in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006;6:857–866. - PubMed
-
- Gaál Z, Oláh E. MicroRNAs and their role in malignant hematologic diseases. Orv Hetil. 2012;153:2051–2059. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

