Captures of MFO-resistant Cydia pomonella adults as affected by lure, crop management system and flight
- PMID: 26497943
- PMCID: PMC4762241
- DOI: 10.1017/S0007485315000772
Captures of MFO-resistant Cydia pomonella adults as affected by lure, crop management system and flight
Abstract
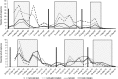
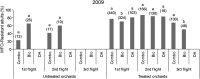
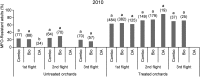
The main resistance mechanism of codling moth (Cydia pomonella) in the tree fruit area of Lleida (NE Spain) is multifunction oxidases (MFO). We studied the frequency of MFO-resistant adults captured by different lures, with and without pear ester, and flights in orchards under different crop management systems. The factor year affected codling moth MFO-resistance level, particularly in the untreated orchards, highlighting the great influence of codling moth migration on the spread of resistance in field populations. Chemical treatments and adult flight were also very important but mating disruption technique showed no influence. The second adult flight showed the highest frequency, followed by the first flight and the third flight. In untreated orchards, there were no significant differences in the frequency of MFO-resistant individuals attracted by Combo and BioLure. Red septa lures baited with pear ester (DA) captured sufficient insects only in the first generation of 2010, obtaining a significantly lower proportion of MFO-resistant adults than Combo and BioLure. In the chemically treated orchards, in 2009 BioLure caught a significantly lower proportion of MFO-resistant adults than Combo during the first and third flight, and also than DA during the first flight. No significant differences were found between the lures or flights in 2010. These results cannot support the idea of a higher attractiveness of the pear ester for MFO-resistant adults in the field but do suggest a high influence of the response to the attractant depending on the management of the orchard, particularly with regard to the use of chemical insecticides.
Keywords: Cydia pomonella; adult flight; codlemone; crop management; mixed function oxidases; monitoring; pear ester.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparison of lures loaded with codlemone and pear ester for capturing codling moths, Cydia pomonella, in apple and pear orchards using mating disruption.J Insect Sci. 2010;10:139. doi: 10.1673/031.010.13901. J Insect Sci. 2010. PMID: 20883133 Free PMC article.
-
Improved monitoring of female codling moth (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae) with pear ester plus acetic acid in sex pheromone-treated orchards.Environ Entomol. 2010 Aug;39(4):1283-90. doi: 10.1603/EN10034. Environ Entomol. 2010. PMID: 22127179
-
Monitoring codling moth (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae) in sex pheromone-treated orchards with (E)-4,8-dimethyl-1,3,7-nonatriene or pear ester in combination with codlemone and acetic acid.Environ Entomol. 2012 Apr;41(2):407-14. doi: 10.1603/EN11310. Environ Entomol. 2012. PMID: 22507016
-
Codling moth management and chemical ecology.Annu Rev Entomol. 2008;53:503-22. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ento.53.103106.093323. Annu Rev Entomol. 2008. PMID: 17877451 Review.
-
[Research advances in the effects of host plant volatiles on Cydia pomonella behaviors and the application of the volatiles in pest control].Ying Yong Sheng Tai Xue Bao. 2010 Sep;21(9):2434-40. Ying Yong Sheng Tai Xue Bao. 2010. PMID: 21265171 Review. Chinese.
References
-
- Barrett B.A. (2008) Assessment of methoxyfenozide exposure on the sexual attractiveness and responsiveness of adult codling moth, Cydia pomonella (L.), in small orchard blocks. Pest Management Science 64, 916–922. - PubMed
-
- Barrett B.A. (2010) Exposure to methoxyfenozide treated surfaces reduces the responsiveness of adult male codling moth (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae) to codlemone and pear ester lures in a wind tunnel. Journal of Economic Entomology 103, 1704–1710. - PubMed
-
- Boivin T., Chabert-d'Hières C., Bouvier J.C., Beslay D. & Sauphanor B. (2001) Pleiotropy of insecticide resistance in the codling moth, Cydia pomonella. Entomolgia Experimentalis et Applicata 99, 381–386.
-
- Boivin T., Bouvier J.C., Chadoeuf J., Beslay D. & Sauphanor B. (2003a) Constraints on adaptative mutations in the codling moth Cydia pomonella (L.): measuring fitness trade-offs and natural selection. Heredity 90, 107–113. - PubMed
-
- Boivin T., Bouvier J.C., Beslay D. & Sauphanor B. (2003b) Phenological segregation of insecticide-resistant genotypes in the codling moth Cydia pomonella (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae): a case study of ecological divergences associated with adaptive changes in populations. Genetical Research 81, 177. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

