Utility of untimed single urine protein/creatinine ratio as a substitute for 24-h proteinuria for assessment of proteinuria in systemic lupus erythematosus
- PMID: 26497948
- PMCID: PMC4619322
- DOI: 10.1186/s13075-015-0808-x
Utility of untimed single urine protein/creatinine ratio as a substitute for 24-h proteinuria for assessment of proteinuria in systemic lupus erythematosus
Abstract
Introduction: In this study, we determined: (1) the utility of an untimed sample of urine protein/creatinine ratio (PCR) as a screening test for proteinuria, (2) its ability to accurately measure proteinuria, and (3) cutoff values for PCR predicting protein content in a 24-h urine collection sample (24hP) of 0.5, 1.0, and 2.0 g/day.
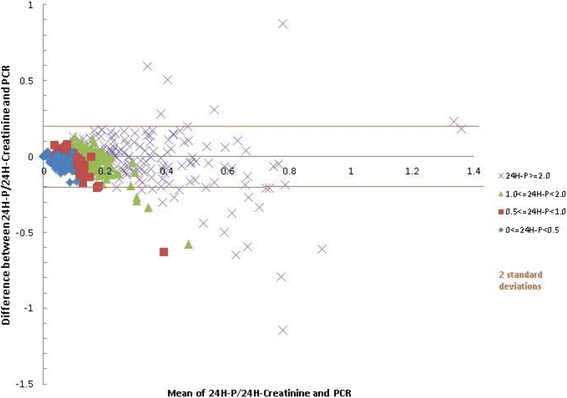
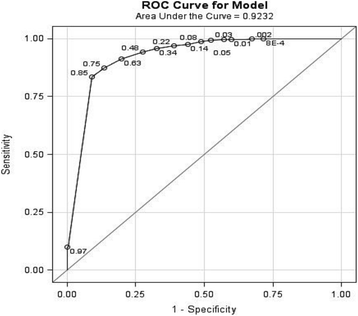
Methods: Analysis was performed on data from a single lupus cohort (2008-2014). Proteinuria was measured in a 24hP and with PCR. On the basis of 24hP, samples were divided into 4 groups: group 1, <0.5 g/day; group 2, 0.5-0.99 g/day; group 3, 1-1.99 g/day; and group 4, ≥2 g/day. To determine the validity of PCR in screening for proteinuria, the Pearson correlation coefficient was determined for the urine samples with normal PCR (<0.05 g/mmol) and normal 24hP (<0.5 g/day). The sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value (PPV), and negative predictive value (NPV) of PCR were calculated. To determine the ability of PCR to accurately measure the level of proteinuria, in addition to the correlation between 24hP and PCR, agreement was determined by intraclass correlation coefficient, concordance correlation coefficient, and Bland-Altman plot between 24hP/24hC and PCR. The best cutoffs for PCR predicting a 24hP of 0.5, 1.0, and 2.0 g/day were determined with the receiver operating characteristic curve.
Results: The correlation of the samples with normal PCR as well as 24hP (n = 552) was 0.29 (p < 0.0001). PCR sensitivity and specificity against 24hP were 91 % and 83 %, respectively. The PPV was 82.5 %, and the NPV was 91.4 %. The correlation for all samples (n = 1233) was high, but low to moderate for groups 1, 2, 3, and 4. The agreement for all samples was appropriate but poor for groups 1, 2, 3, and 4. PCR cutoffs for 24hP of 0.5, 1.0, and 2.0 g/day were 0.08, 0.16, and 0.35 g/mmol, respectively.
Conclusions: PCR can be used as a screening test for proteinuria, and the best cutoff value to predict a 24hP of 0.5 g/day is 0.08 g/mmol (800 mg/g). The accurate level of proteinuria should be measured by the gold standard test, 24hP.
Figures

References
-
- Dye-Torrington D, Urowitz MB, Ibanez D, Gladman DD. Late versus early development of lupus nephritis [abstract] Arthritis Rheum. 2011;63(Suppl 10):2284.
-
- Cameron JS. Lupus nephritis. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1999;10(2):413–24. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

