Consumer response to media information: the case of grapefruit-medicine interaction
- PMID: 26497966
- PMCID: PMC4623079
- DOI: 10.1186/s13561-015-0069-z
Consumer response to media information: the case of grapefruit-medicine interaction
Abstract
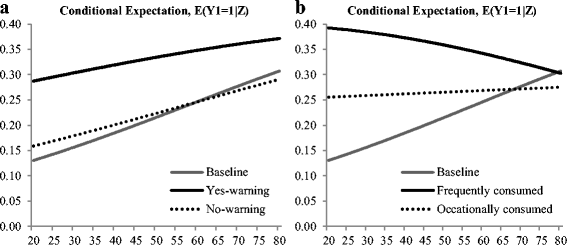
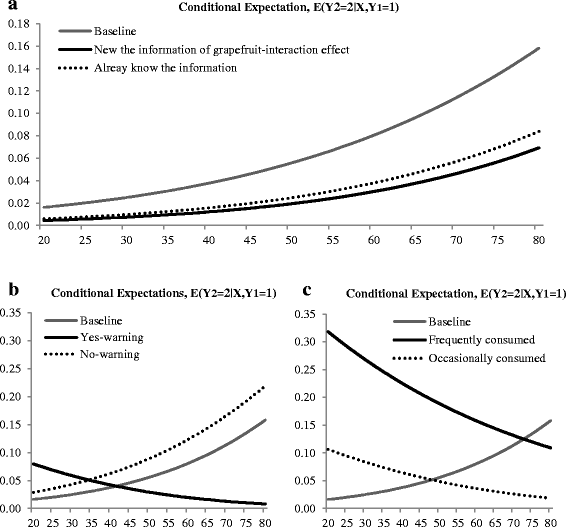
This study measured the effect of media exposure on grapefruit/grapefruit juice consumption changes, in particular grapefruit-medicine interaction. Respondents' attitudes about health news on television and the internet were measured to account for consumers exposed versus not exposed to such information. Results of a sample selection model show that consumer attitudes toward health news were significantly related to exposure to media information. Also, news exposure about grapefruit-medicine interaction has a tendency to result in reduced grapefruit consumption. Consumers who are directly affected by the medication interaction significantly react to the news, and the effect varies by age. Even though consumer's age was positively related to the probability of increased grapefruit consumption, when consumers took the medication, consumer's age was negatively related to the probability of increased grapefruit consumption.
Keywords: Food-medicine interaction; Grapefruit; Interaction terms; Non-linear model; Sample selection.
Figures
References
-
- Dillaway R, Messer KD, Bernard JC, Kaiser HM. Do consumer responses to media food safety information last? Appl Econ Perspect Policy. 2011;33:363–383. doi: 10.1093/aepp/ppr019. - DOI
-
- Piggot NE, Marsh TL. Does food safety information impact US meat demand? Am J Agr Econ. 2004;86:154–174. doi: 10.1111/j.0092-5853.2004.00569.x. - DOI
-
- Adhikari M, Paudel L, Houston JE, Paudel KP, Bukenya J. The impact of cholesterol information on meat demand: application of an updated cholesterol index. J Food Distribution Res. 2006;37:60–69.
-
- Brown DJ, Schrader LF. Cholesterol information and shell egg consumption. Am J Agr Econ. 1990;72:548–555. doi: 10.2307/1243023. - DOI
-
- Dentoni D, Tonsor G, Calantone R, Peterson HC. Animal welfare practices along the food chain: how does negative and positive information affect consumers? J Food Prod Market. 2011;17:279–302. doi: 10.1080/10454446.2011.548720. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

