Ketamine suppresses hypoxia-induced inflammatory responses in the late-gestation ovine fetal kidney cortex
- PMID: 26497972
- PMCID: PMC4771785
- DOI: 10.1113/JP271066
Ketamine suppresses hypoxia-induced inflammatory responses in the late-gestation ovine fetal kidney cortex
Abstract
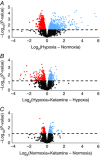
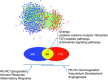
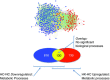
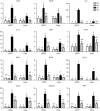
Acute fetal hypoxia is a form of fetal stress that stimulates renal vasoconstriction and ischaemia as a consequence of the physiological redistribution of combined ventricular output. Because of the potential ischaemia-reperfusion injury to the kidney, we hypothesized that it would respond to hypoxia with an increase in the expression of inflammatory genes, and that ketamine (an N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonist) would reduce or block this response. Hypoxia was induced for 30 min in chronically catheterized fetal sheep (125 ± 3 days), with or without ketamine (3 mg kg(-1)) administered intravenously to the fetus 10 min prior to hypoxia. Gene expression in fetal kidney cortex collected 24 h after the onset of hypoxia was analysed using ovine Agilent 15.5k array and validated with qPCR and immunohistochemistry in four groups of ewes: normoxic control, normoxia + ketamine, hypoxic control and hypoxia + ketamine (n = 3-4 per group). Significant differences in gene expression between groups were determined with t-statistics using the limma package for R (P ≤ 0.05). Enriched biological processes for the 427 upregulated genes were immune and inflammatory responses and for the 946 downregulated genes were metabolic processes. Ketamine countered the effects of hypoxia on upregulated immune/inflammatory responses as well as the downregulated metabolic responses. We conclude that our transcriptomics modelling predicts that hypoxia activates inflammatory pathways and reduces metabolism in the fetal kidney cortex, and ketamine blocks or ameliorates this response. The results suggest that ketamine may have therapeutic potential for protection from ischaemic renal damage.
© 2015 The Authors. The Journal of Physiology © 2015 The Physiological Society.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of ketamine on the fetal transcriptomic response to umbilical cord occlusion: comparison with hypoxic hypoxia in the cerebral cortex.J Physiol. 2018 Dec;596(23):6063-6077. doi: 10.1113/JP275661. Epub 2018 Jul 6. J Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29882596 Free PMC article.
-
Ketamine decreases inflammatory and immune pathways after transient hypoxia in late gestation fetal cerebral cortex.Physiol Rep. 2016 Mar;4(6):e12741. doi: 10.14814/phy2.12741. Epub 2016 Mar 31. Physiol Rep. 2016. PMID: 27033443 Free PMC article.
-
Ketamine Reduces Inflammation Pathways in the Hypothalamus and Hippocampus Following Transient Hypoxia in the Late-Gestation Fetal Sheep.Front Physiol. 2019 Jan 7;9:1858. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2018.01858. eCollection 2018. Front Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30666211 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroprotection by ketamine: a review of the experimental and clinical evidence.J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2010 Feb;24(1):131-42. doi: 10.1053/j.jvca.2009.05.008. Epub 2009 Jul 29. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2010. PMID: 19640746 Review. No abstract available.
-
[Effect of ketamine on global cerebral ischemia].Anaesthesist. 1997 Mar;46 Suppl 1:S61-4. doi: 10.1007/pl00002467. Anaesthesist. 1997. PMID: 9163281 Review. German.
Cited by
-
Ketamine modulates fetal hemodynamic and endocrine responses to umbilical cord occlusion.Physiol Rep. 2016 Sep;4(17):e12962. doi: 10.14814/phy2.12962. Physiol Rep. 2016. PMID: 27597770 Free PMC article.
-
Transfer of oral bacteria to the fetus during late gestation.Sci Rep. 2021 Jan 12;11(1):708. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-80653-y. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33436911 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of anesthetic agents on inflammation in Caco-2, HK-2 and HepG2 cells.Exp Ther Med. 2021 May;21(5):487. doi: 10.3892/etm.2021.9918. Epub 2021 Mar 16. Exp Ther Med. 2021. PMID: 33790996 Free PMC article.
-
Ketamine ameliorates hypoxia-induced endothelial injury in human umbilical vein endothelial cells.Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2020 Sep 11;75:e1865. doi: 10.6061/clinics/2020/e1865. eCollection 2020. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2020. PMID: 32935825 Free PMC article.
-
Considerations in selecting postoperative analgesia for pregnant sheep following fetal instrumentation surgery.Anim Front. 2019 Jun 25;9(3):60-67. doi: 10.1093/af/vfz019. eCollection 2019 Jul. Anim Front. 2019. PMID: 32002263 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Anand KJ (2007). Pharmacological approaches to the management of pain in the neonatal intensive care unit. J Perinatol 27 (Suppl. 1), S4–S11. - PubMed
-
- Chang EI & Wood CE (2013). Ketamine decreases apoptotic and inflammatory gene expression in fetal hippocampus exposed to global acute hypoxic hypoxia In Reproductive Sciences, Vol. 20, pp. F089.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

