Host JDP2 expression in the bone marrow contributes to metastatic spread
- PMID: 26497998
- PMCID: PMC4741961
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.5648
Host JDP2 expression in the bone marrow contributes to metastatic spread
Abstract
The c-Jun Dimerization Protein 2, JDP2, is a basic leucine zipper protein member of the activator protein-1 (AP-1) family of transcription factors. JDP2 typically suppresses gene transcription through multiple mechanisms and plays a dual role in multiple cellular processes, including cell differentiation and proliferation which is dependent on AP-1 function. Whereas the role of JDP2 expression within cancer cells has been studied, its role in stromal cells at the tumor microenvironment is largely unknown. Here we show that mice lacking JDP2 (JDP2-/-) display a reduced rate of metastasis in Lewis lung carcinoma (LLC) and polyoma middle T-antigen (PyMT) breast carcinoma mouse models. The replacement of wild-type bone marrow derived cells (BMDCs) with JDP2-deficient BMDCs recapitulates the metastatic phenotype of JDP2-/- tumor-bearing mice. In vitro, conditioned medium of wild-type BMDCs significantly potentiates the migration and invasion capacity of LLC cells as compared to that of JDP2-/- BMDCs. Furthermore, wild-type BMDCs secrete CCL5, a chemokine known to contribute to metastasis, to a greater extent than JDP2-/- BMDCs. The supplementation of CCL5 in JDP2-/- BMDC conditioned medium was sufficient to potentiate the invasion capacity of LLC. Overall, this study suggests that JDP2-expressing BMDCs within the tumor microenvironment contribute to metastatic spread.
Keywords: CCL5; JDP2; Lewis lung carcinoma; bone marrow derived cells; metastasis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
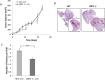
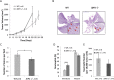

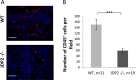
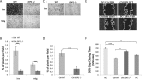
References
-
- Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell. 2011;144:646–674. - PubMed
-
- Hanahan D, Coussens LM. Accessories to the crime: functions of cells recruited to the tumor microenvironment. Cancer cell. 2012;21:309–322. - PubMed
-
- Houghton AM. The paradox of tumor-associated neutrophils: fueling tumor growth with cytotoxic substances. Cell Cycle. 2010;9:1732–1737. - PubMed
-
- Lewis CE, Pollard JW. Distinct role of macrophages in different tumor microenvironments. Cancer Res. 2006;66:605–612. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

