Antimicrobial potential of 27 plants consumed by chimpanzees (Pan troglodytes verus Blumenbach) in Ivory Coast
- PMID: 26498034
- PMCID: PMC4618953
- DOI: 10.1186/s12906-015-0918-7
Antimicrobial potential of 27 plants consumed by chimpanzees (Pan troglodytes verus Blumenbach) in Ivory Coast
Abstract
Background: Due to their genetic proximity, chimpanzees share with human several diseases including bacterial, fungal and viral infections, such as candidiasis, acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS), Ebola virus disease. However, in its natural environment, chimpanzees are tolerant to several pathogens including simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV), virus related to human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) that contribute to the emergence of opportunistic diseases such as microbial infections.
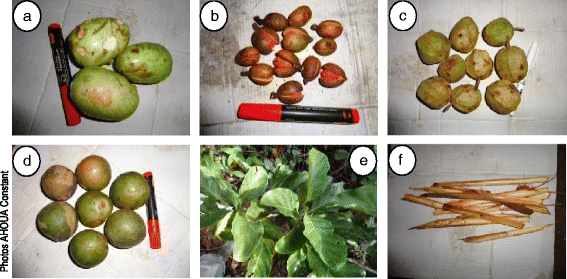
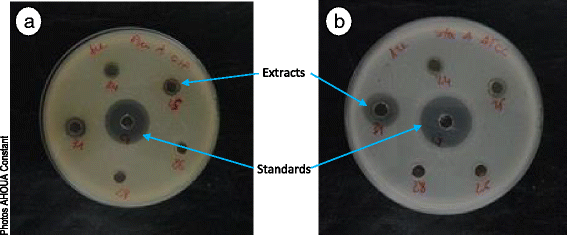
Methods: Twenty seven species of plants consumed by chimpanzees were evaluated for their antimicrobial potential against Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Staphylococcus aureus, Candida albicans, Candida tropicalis and Candida glabrata using the agar diffusion technique and micro-dilution in 96-well plates. In total 132 extracts (33 dichloromethane, 33 methanol, 33 ethyl acetate and 33 aqueous) were tested.
Results: The results showed that 24 extracts (18 %) showed activity against bacteria and 6 extracts (5 %) were active against yeasts. The minimal inhibitory concentrations (MICs) values of active extracts ranged between 23 and 750 μg/ml for bacteria and between 188 and 1500 μg/ml for yeasts.
Conclusion: Tristemma coronatum was the most promising on the studied microorganisms followed by Beilschmiedia mannii. The extracts of the two plants indicated by chimpanzees have potential for antimicrobial use in human.
Figures

References
-
- Diallo A. Etude de la phytochimie et des activités biologiques de Syzygium guineense Willd. (Myrtaceae) Université de Bamako, Mali: Faculté de Médecine, de Pharmacie et d’Odoto-Stomatologie; 2005.
-
- Blythe S. An introduction to medicines from plants. 1999.
-
- Chanda S, Rakholiya K. Combination therapy: Synergism between natural plant extracts and antibiotics against infectious diseases. In: Méndez-Vials A, editor. Science against microbiology pathogens: communicating current research and technological advances. 2011. pp. 520–9.
-
- Soro D, Kone MW, Kamanzi K. Evaluation des activités antimicrobiennes et anti-radicaux libres de quelques taxons bioactifs de Côte d’Ivoire. Eur J Sci Res. 2010;40:307–17.
-
- Akinyemi KO, Oladapo O, Okwara CE, Ibe CC, Fasure KA. Screening of crude extracts of six medicinal plants used in South-West Nigerian unorthodox medicine for anti-methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus activity. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2005;5:6. doi: 10.1186/1472-6882-5-6. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

