Role of GADD45a in murine models of radiation- and bleomycin-induced lung injury
- PMID: 26498248
- PMCID: PMC4683317
- DOI: 10.1152/ajplung.00146.2014
Role of GADD45a in murine models of radiation- and bleomycin-induced lung injury
Abstract
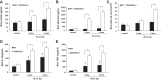
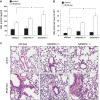
We previously reported protective effects of GADD45a (growth arrest and DNA damage-inducible gene 45 alpha) in murine ventilator-induced lung injury (VILI) via effects on Akt-mediated endothelial cell signaling. In the present study we investigated the role of GADD45a in separate murine models of radiation- and bleomycin-induced lung injury. Initial studies of wild-type mice subjected to single-dose thoracic radiation (10 Gy) confirmed a significant increase in lung GADD45a expression within 24 h and persistent at 6 wk. Mice deficient in GADD45a (GADD45a(-/-)) demonstrated increased susceptibility to radiation-induced lung injury (RILI, 10 Gy) evidenced by increased bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) fluid total cell counts, protein and albumin levels, and levels of inflammatory cytokines compared with RILI-challenged wild-type animals at 2 and 4 wk. Furthermore, GADD45a(-/-) mice had decreased total and phosphorylated lung Akt levels both at baseline and 6 wk after RILI challenge relative to wild-type mice while increased RILI susceptibility was observed in both Akt(+/-) mice and mice treated with an Akt inhibitor beginning 1 wk prior to irradiation. Additionally, overexpression of a constitutively active Akt1 transgene reversed RILI-susceptibility in GADD45a(-/-) mice. In separate studies, lung fibrotic changes 2 wk after treatment with bleomycin (0.25 U/kg IT) was significantly increased in GADD45a(-/-) mice compared with wild-type mice assessed by lung collagen content and histology. These data implicate GADD45a as an important modulator of lung inflammatory responses across different injury models and highlight GADD45a-mediated signaling as a novel target in inflammatory lung injury clinically.
Keywords: Akt; GADD45a; bleomycin; lung fibrosis; lung injury; radiation pneumonitis.
Copyright © 2015 the American Physiological Society.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Role of growth arrest and DNA damage-inducible α in Akt phosphorylation and ubiquitination after mechanical stress-induced vascular injury.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2011 Nov 1;184(9):1030-40. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201103-0447OC. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2011. PMID: 21816939 Free PMC article.
-
GADD45a is a novel candidate gene in inflammatory lung injury via influences on Akt signaling.FASEB J. 2009 May;23(5):1325-37. doi: 10.1096/fj.08-119073. Epub 2009 Jan 5. FASEB J. 2009. PMID: 19124556 Free PMC article.
-
Exercise Reduces Lung Fibrosis Involving Serotonin/Akt Signaling.Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2016 Jul;48(7):1276-84. doi: 10.1249/MSS.0000000000000907. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2016. PMID: 26895395
-
Regulatory T Cells: An Emerging Player in Radiation-Induced Lung Injury.Front Immunol. 2020 Aug 4;11:1769. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01769. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32849634 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sphingolipids as a Novel Therapeutic Target in Radiation-Induced Lung Injury.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2021 Sep;79(3):509-516. doi: 10.1007/s12013-021-01022-8. Epub 2021 Aug 9. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2021. PMID: 34370281 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
UCHL1 Regulates Radiation Lung Injury via Sphingosine Kinase-1.Cells. 2023 Oct 5;12(19):2405. doi: 10.3390/cells12192405. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37830619 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of GADD45A on Radiation Biodosimetry Using Mouse Peripheral Blood.Radiat Res. 2023 Sep 1;200(3):296-306. doi: 10.1667/RADE-23-00052.1. Radiat Res. 2023. PMID: 37421415 Free PMC article.
-
DNA hypomethylation-mediated upregulation of GADD45B facilitates airway inflammation and epithelial cell senescence in COPD.J Adv Res. 2025 Feb;68:201-214. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2024.02.005. Epub 2024 Feb 10. J Adv Res. 2025. PMID: 38342401 Free PMC article.
-
Deficiency of the Deubiquitinase UCHL1 Attenuates Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension.Circulation. 2024 Jul 23;150(4):302-316. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.123.065304. Epub 2024 May 2. Circulation. 2024. PMID: 38695173 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of eNAMPT/TLR4 signaling in murine radiation pneumonitis: protection by eNAMPT neutralization.Transl Res. 2022 Jan;239:44-57. doi: 10.1016/j.trsl.2021.06.002. Epub 2021 Jun 15. Transl Res. 2022. PMID: 34139379 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen Y, Ma X, Zhang M, Wang X, Wang C, Wang H, Guo P, Yuan W, Rudolph KL, Zhan Q, Ju Z. Gadd45a regulates hematopoietic stem cell stress responses in mice. Blood 123: 851–862, 2012. - PubMed
-
- Corn PG, El-Deiry WS. Microarray analysis of p53-dependent gene expression in response to hypoxia and DNA damage. Cancer Biol Ther 6: 1858–1866, 2007. - PubMed
-
- Culine S, Kramar A, Theodore C, Geoffrois L, Chevreau C, Biron P, Nguyen BB, Heron JF, Kerbrat P, Caty A, Delva R, Fargeot P, Fizazi K, Bouzy J, Droz JP. Randomized trial comparing, bleomycin/etoposide/cisplatin with alternating cisplatin/cyclophosphamide/doxorubicin and vinblastine/bleomycin regimens of chemotherapy for patients with intermediate- and poor-risk metastatic nonseminomatous germ cell tumors: Genito-Urinary Group of the French Federation of Cancer Centers Trial T93MP. J Clin Oncol 26: 421–427, 2008. - PubMed
-
- de Wit R, Roberts JT, Wilkinson PM, de Mulder PH, Mead GM, Fossa SD, Cook P, de Prijck L, Stenning S, Collette L. Equivalence of three or four cycles of bleomycin, etoposide, and cisplatin chemotherapy and of a 3- or 5-day schedule in good-prognosis germ cell cancer: a randomized study of the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer Genitourinary Tract Cancer Cooperative Group and the Medical Research Council. J Clin Oncol 19: 1629–1640, 2001. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

