Five miRNAs Considered as Molecular Targets for Predicting Esophageal Cancer
- PMID: 26498375
- PMCID: PMC4627364
- DOI: 10.12659/msm.895001
Five miRNAs Considered as Molecular Targets for Predicting Esophageal Cancer
Abstract
Background: Esophageal cancer (EC) is one of the most aggressive malignant gastrointestinal tumors; however the traditional therapies for EC are not effective enough. Great improvements are needed to explore new and valid treatments for EC. We aimed to screen the differentially expressed miRNAs (DEMs) in esophageal cancer and explore the pathogenesis of esophageal cancer along with functions and pathways of the target genes.
Material and methods: miRNA high-throughput sequencing data were downloaded from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA), then the DEMs underwent principal component analysis (PCA) based on their expression value. Following that, TargetScan software was used to predict the target genes, and enrichment analysis and pathway annotation of these target genes were done by DAVID and KEGG, respectively. Finally, survival analysis between the DEMs and patient survival time was done, and the miRNAs with prediction potential were identified.
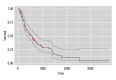
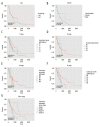
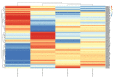
Results: A total of 140 DEMs were obtained, 113 miRNAs were up-regulated including hsa-mir-153-2, hsa-mir-92a-1 and hsa-mir-182; while 27 miRNAs were down-regulated including hsa-mir comprising 29a, hsa-mir-100 and hsa-mir-139 and so on. Five miRNAs (hsa-mir-103-1, hsa-mir-18a, hsa-mir-324, hsa-mir-369 and hsa-mir-320b-2) with diagnostic and preventive potential were significantly correlated with survival time.
Conclusions: The crucial molecular targets such as p53 may provide great clinical value in treatment, as well to provide new ideas for esophageal cancer therapy. The target genes of miRNA were found to play key roles in protein phosphorylation, and the functions of the target genes during protein phosphorylation should be further studied to explore novel treatment of EC.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

