RLIP76 regulates Arf6-dependent cell spreading and migration by linking ARNO with activated R-Ras at recycling endosomes
- PMID: 26498519
- PMCID: PMC4644438
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2015.10.064
RLIP76 regulates Arf6-dependent cell spreading and migration by linking ARNO with activated R-Ras at recycling endosomes
Abstract
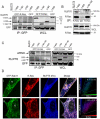
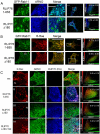
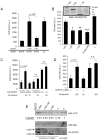
R-Ras small GTPase enhances cell spreading and motility via RalBP1/RLIP76, an R-Ras effector that links GTP-R-Ras to activation of Arf6 and Rac1 GTPases. Here, we report that RLIP76 performs these functions by binding cytohesin-2/ARNO, an Arf GTPase guanine exchange factor, and connecting it to R-Ras at recycling endosomes. RLIP76 formed a complex with R-Ras and ARNO by binding ARNO via its N-terminus (residues 1-180) and R-Ras via residues 180-192. This complex was present in Rab11-positive recycling endosomes and the presence of ARNO in recycling endosomes required RLIP76, and was not supported by RLIP76(Δ1-180) or RLIP76(Δ180-192). Spreading and migration required RLIP76(1-180), and RLIP76(Δ1-180) blocked ARNO recruitment to recycling endosomes, and spreading. Arf6 activation with an ArfGAP inhibitor overcame the spreading defects in RLIP76-depleted cells or cells expressing RLIP76(Δ1-180). Similarly, RLIP76(Δ1-180) or RLIP76(Δ180-192) suppressed Arf6 activation. Together these results demonstrate that RLIP76 acts as a scaffold at recycling endosomes by binding activated R-Ras, recruiting ARNO to activate Arf6, thereby contributing to cell spreading and migration.
Keywords: Migration; Ras; Recycling endosome; Small GTPase; Spreading.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The RLIP76 N-terminus binds ARNO to regulate PI 3-kinase, Arf6 and Rac signaling, cell spreading and migration.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014 Nov 28;454(4):560-5. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2014.10.114. Epub 2014 Oct 30. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014. PMID: 25450693 Free PMC article.
-
RLIP76 (RalBP1) is an R-Ras effector that mediates adhesion-dependent Rac activation and cell migration.J Cell Biol. 2006 Sep 11;174(6):877-88. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200603111. J Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16966426 Free PMC article.
-
ARF-GEF cytohesin-2/ARNO regulates R-Ras and α5-integrin recycling through an EHD1-positive compartment.Mol Biol Cell. 2015 Nov 15;26(23):4265-79. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E15-05-0278. Epub 2015 Sep 16. Mol Biol Cell. 2015. PMID: 26378252 Free PMC article.
-
Cell motility: ARNOand ARF6 at the cutting edge.Curr Biol. 2001 Oct 30;11(21):R875-7. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(01)00521-8. Curr Biol. 2001. PMID: 11696346 Review.
-
GTPases Rac1 and Ras Signaling from Endosomes.Prog Mol Subcell Biol. 2018;57:65-105. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-96704-2_3. Prog Mol Subcell Biol. 2018. PMID: 30097772 Review.
Cited by
-
RLIP inhibition suppresses breast-to-lung metastasis.Cancer Lett. 2019 Apr 10;447:24-32. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2019.01.023. Epub 2019 Jan 23. Cancer Lett. 2019. PMID: 30684594 Free PMC article.
-
The RAS-Effector Interface: Isoform-Specific Differences in the Effector Binding Regions.PLoS One. 2016 Dec 9;11(12):e0167145. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0167145. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27936046 Free PMC article.
-
TBC1D10C is a cytoskeletal functional linker that modulates cell spreading and phagocytosis in macrophages.Sci Rep. 2021 Oct 22;11(1):20946. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-00450-z. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34686741 Free PMC article.
-
A family affair: A Ral-exocyst-centered network links Ras, Rac, Rho signaling to control cell migration.Small GTPases. 2019 Sep;10(5):323-330. doi: 10.1080/21541248.2017.1310649. Epub 2017 May 12. Small GTPases. 2019. PMID: 28498728 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metastasis of breast tumor cells to brain is suppressed by targeting RLIP alone and in combination with 2'-Hydroxyflavanone.Cancer Lett. 2018 Dec 1;438:144-153. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2018.09.015. Epub 2018 Sep 15. Cancer Lett. 2018. PMID: 30223070 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ridley AJ, Schwartz MA, Burridge K, Firtel RA, Ginsberg MH, Borisy G, Parsons JT, Horwitz AR. Cell migration: integrating signals from front to back. Science. 2003;302:1704–1709. - PubMed
-
- Schwartz MA, Horwitz AR. Integrating adhesion, protrusion, and contraction during cell migration. Cell. 2006;125:1223–1225. - PubMed
-
- Pollard TD, Borisy GG. Cellular motility driven by assembly and disassembly of actin filaments. Cell. 2003;112:453–465. - PubMed
-
- Radhakrishna H, Al-Awar O, Khachikian Z, Donaldson JG. ARF6 requirement for Rac ruffling suggests a role for membrane trafficking in cortical actin rearrangements. Journal of Cell Science. 1999;112(Pt 6):855–866. - PubMed
-
- Song J, Khachikian Z, Radhakrishna H, Donaldson JG. Localization of endogenous ARF6 to sites of cortical actin rearrangement and involvement of ARF6 in cell spreading. J Cell Sci. 1998;111(Pt 15):2257–2267. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

