Genetics, sleep and memory: a recall-by-genotype study of ZNF804A variants and sleep neurophysiology
- PMID: 26498712
- PMCID: PMC4619339
- DOI: 10.1186/s12881-015-0244-4
Genetics, sleep and memory: a recall-by-genotype study of ZNF804A variants and sleep neurophysiology
Abstract
Background: Schizophrenia is a complex, polygenic disorder for which over 100 genetic variants have been identified that correlate with diagnosis. However, the biological mechanisms underpinning the different symptom clusters remain undefined. The rs1344706 single nucleotide polymorphism within ZNF804A was among the first genetic variants found to be associated with schizophrenia. Previously, neuroimaging and cognitive studies have revealed several associations between rs1344706 and brain structure and function. The aim of this study is to use a recall-by-genotype (RBG) design to investigate the biological basis for the association of ZNF804A variants with schizophrenia. A RBG study, implemented in a population cohort, will be used to evaluate the impact of genetic variation at rs1344706 on sleep neurophysiology and procedural memory consolidation in healthy participants.
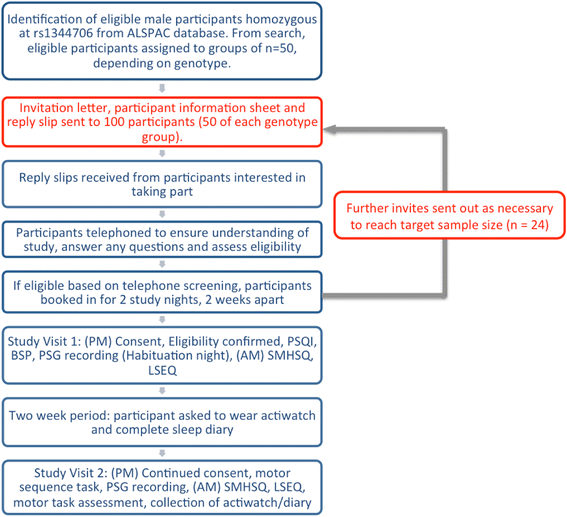
Methods/design: Participants will be recruited from the Avon Longitudinal Study of Parents and Children (ALSPAC) on the basis of genotype at rs1344706 (n = 24). Each participant will be asked to take part in two nights of in-depth sleep monitoring (polysomnography) allowing collection of neurophysiological sleep data in a manner not amenable to large-scale study. Sleep questionnaires will be used to assess general sleep quality and subjective sleep experience after each in-house recording. A motor sequencing task (MST) will be performed before and after the second night of polysomnography. In order to gather additional data about habitual sleep behaviour participants will be asked to wear a wrist worn activity monitor (actiwatch) and complete a sleep diary for two weeks.
Discussion: This study will explore the biological function of ZNF804A genotype (rs1344706) in healthy volunteers by examining detailed features of sleep architecture and physiology in relation to motor learning. Using a RBG approach will enable us to collect precise and detailed phenotypic data whilst achieving an informative biological gradient. It would not be feasible to collect such data in the large sample sizes that would be required under a random sampling scheme. By dissecting the role of individual variants associated with schizophrenia in this way, we can begin to unravel the complex genetic mechanisms of psychiatric disorders and pave the way for future development of novel therapeutic approaches.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Schizophrenia-associated variation at ZNF804A correlates with altered experience-dependent dynamics of sleep slow waves and spindles in healthy young adults.Sleep. 2021 Dec 10;44(12):zsab191. doi: 10.1093/sleep/zsab191. Sleep. 2021. PMID: 34329479 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of ZNF804A in human brain and alterations in schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and major depressive disorder: a novel transcript fetally regulated by the psychosis risk variant rs1344706.JAMA Psychiatry. 2014 Oct;71(10):1112-20. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2014.1079. JAMA Psychiatry. 2014. PMID: 25162540 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence that schizophrenia risk variation in the ZNF804A gene exerts its effects during fetal brain development.Am J Psychiatry. 2012 Dec;169(12):1301-8. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2012.11121845. Am J Psychiatry. 2012. PMID: 23212061
-
The schizophrenia risk gene ZNF804A: clinical associations, biological mechanisms and neuronal functions.Mol Psychiatry. 2017 Jul;22(7):944-953. doi: 10.1038/mp.2017.19. Epub 2017 Mar 14. Mol Psychiatry. 2017. PMID: 28289284 Review.
-
Bioinformatic analyses and conceptual synthesis of evidence linking ZNF804A to risk for schizophrenia and bipolar disorder.Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2015 Jan;168B(1):14-35. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.b.32284. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2015. PMID: 25522715 Review.
Cited by
-
Balancing scientific interests and the rights of participants in designing a recall by genotype study.Eur J Hum Genet. 2021 Jul;29(7):1146-1157. doi: 10.1038/s41431-021-00860-7. Epub 2021 May 13. Eur J Hum Genet. 2021. PMID: 33981014 Free PMC article.
-
From target discovery to clinical drug development with human genetics.Nature. 2023 Aug;620(7975):737-745. doi: 10.1038/s41586-023-06388-8. Epub 2023 Aug 23. Nature. 2023. PMID: 37612393 Review.
-
Variants in the fetal genome near FLT1 are associated with risk of preeclampsia.Nat Genet. 2017 Aug;49(8):1255-1260. doi: 10.1038/ng.3895. Epub 2017 Jun 19. Nat Genet. 2017. PMID: 28628106
-
Schizophrenia-associated variation at ZNF804A correlates with altered experience-dependent dynamics of sleep slow waves and spindles in healthy young adults.Sleep. 2021 Dec 10;44(12):zsab191. doi: 10.1093/sleep/zsab191. Sleep. 2021. PMID: 34329479 Free PMC article.
-
Formalising recall by genotype as an efficient approach to detailed phenotyping and causal inference.Nat Commun. 2018 Feb 19;9(1):711. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-03109-y. Nat Commun. 2018. PMID: 29459775 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

