A cross-cultural investigation into the dimensional structure and stability of the Barriers to Research and Utilization Scale (BARRIERS Scale)
- PMID: 26498925
- PMCID: PMC4619557
- DOI: 10.1186/s13104-015-1579-9
A cross-cultural investigation into the dimensional structure and stability of the Barriers to Research and Utilization Scale (BARRIERS Scale)
Abstract
Background: It is important that scales exhibit strong measurement properties including those related to the investigation of issues that impact evidence-based practice. The validity of the Barriers to Research Utilization Scale (BARRIERS Scale) has recently been questioned in a systematic review. This study investigated the dimensional structure and stability of the 28 item BARRIERS Scale when completed by three groups of participants from three different cross-cultural environments.
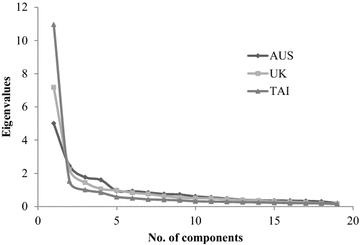
Method: Data from the BARRIERS Scale completed by 696 occupational therapists from Australia (n = 137), Taiwan (n = 413), and the United Kingdom (n = 144) were analysed using principal components analysis, followed by Procrustes Transformation. Poorly fitting items were identified by low communalities, cross-loading, and theoretically inconsistent primary loadings, and were systematically removed until good fit was achieved. The cross-cultural stability of the component structure of the BARRIERS Scale was examined.
Results: A four component, 19 item version of the BARRIERS Scale emerged that demonstrated an improved dimensional fit and stability across the three participant groups. The resulting four components were consistent with the BARRIERS Scale as originally conceptualised.
Conclusion: Findings from the study suggest that the four component, 19 item version of the BARRIERS Scale is a robust and valid measure for identifying barriers to research utilization for occupational therapists in paediatric health care settings across Australia, United Kingdom, and Taiwan. The four component 19 item version of the BARRIERS Scale exhibited good dimensional structure, internal consistency, and stability.
Similar articles
-
Validation of the conceptual research utilization scale: an application of the standards for educational and psychological testing in healthcare.BMC Health Serv Res. 2011 May 19;11:107. doi: 10.1186/1472-6963-11-107. BMC Health Serv Res. 2011. PMID: 21595888 Free PMC article.
-
Research knowledge, attitudes, and practices of pediatric occupational therapists in Australia, the United Kingdom, and Taiwan.J Allied Health. 2010 Summer;39(2):88-94. J Allied Health. 2010. PMID: 20539931
-
Evidence-based practice and research utilisation: perceived research knowledge, attitudes, practices and barriers among Australian paediatric occupational therapists.Aust Occup Ther J. 2011 Jun;58(3):178-86. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1630.2010.00900.x. Epub 2011 Feb 23. Aust Occup Ther J. 2011. PMID: 21599683
-
Determining the psychometric properties of the Enhancing Decision-making Assessment in Midwifery (EDAM) measure in a cross cultural context.BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2016 Apr 28;16:95. doi: 10.1186/s12884-016-0882-3. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2016. PMID: 27126686 Free PMC article.
-
Korean Translation of the Barriers to Research Utilization Scale: Psychometric Testing.Res Theory Nurs Pract. 2017 Aug 1;31(3):233-246. doi: 10.1891/1541-6577.31.3.233. Res Theory Nurs Pract. 2017. PMID: 28793947
References
-
- Turpin M, Higgs J. Clinical reasoning and EBP. In: Hoffmann T, Bennett S, Del Mar C. Chatswood, editors. EBP across the health professions. Australia: Elsevier; 2010. p. 300–317.
-
- Metcalf C, Lewin R, Wisher S, Perry S, Banningan K, Moffett JK. Barriers to implementing the evidence base in four NHS therapies: dietitians, occupational therapists, physiotherapists, speech and language therapists. Physiotherapy. 2001;87(8):433–441. doi: 10.1016/S0031-9406(05)65462-4. - DOI
-
- Thompson DS, Chau JPC, Lopez V. Barriers to, and facilitators of, research utilization: a survey of Hong Kong regsitered nurses. Int J Evid Based Healthc. 2006;4(2):77–82. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources