Development of a Consensus Statement for the Definition, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Acute Exacerbations of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Using the Delphi Technique
- PMID: 26498943
- PMCID: PMC4635174
- DOI: 10.1007/s12325-015-0249-6
Development of a Consensus Statement for the Definition, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Acute Exacerbations of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Using the Delphi Technique
Abstract
Introduction: There is a lack of agreed and established guidelines for the treatment of acute exacerbations of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (AE-IPF). This reflects, in part, the limited evidence-base underpinning the management of AE-IPF. In the absence of high-quality evidence, the aim of this research was to develop a clinician-led consensus statement for the definition, diagnosis and treatment of AE-IPF.
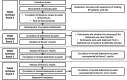
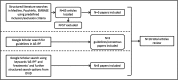
Methods: A literature review was conducted to obtain published material on the definition and treatment of AE-IPF. The results of this review were circulated to an online panel of clinicians for review. Statements were then shared with ten expert respiratory clinicians who regularly treat patients with IPF. A Delphi technique was then used to develop a consensus statement for the definition, diagnosis and treatment of AE-IPF. During the first round of review, clinicians rated the clarity of each statement, the extent to which the statement should be included and provided comments. In two subsequent rounds of review, clinicians were provided with the group median inclusion rating for each statement, and any revised wording of statements to aid clarity. Clinicians were asked to repeat the clarity and inclusion ratings for the revised statements.
Results: The literature review, online panel discussion, and face-to-face meeting generated 65 statements covering the definition, diagnosis, and management of AE-IPF. Following three rounds of blind review, 90% of clinicians agreed 39 final statements. These final statements included a definition of AE-IPF, approach to diagnosis, and treatment options, specifically: supportive measures, use of anti-microbials, immunosuppressants, anti-coagulants, anti-fibrotic therapy, escalation, transplant management, and long-term management including discharge planning.
Conclusion: This clinician-led consensus statement establishes the 'best practice' for the management and treatment of AE-IPF based on current knowledge, evidence, and available treatments.
Keywords: Acute exacerbations; Acute lung injury; Best practice; Consensus statement; Definition; Diagnosis; Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis; Interstitial lung disease; Qualitative research; Treatment.
Figures
References
-
- American Thoracic Society Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: diagnosis and treatment. International consensus statement. American Thoracic Society (ATS), and the European Respiratory Society (ERS) Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2000;161((2 Pt 1)):646–664. - PubMed
-
- American Thoracic S. European Respiratory S American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society International Multidisciplinary Consensus Classification of the Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonias. This joint statement of the American Thoracic Society (ATS), and the European Respiratory Society (ERS) was adopted by the ATS board of directors, June 2001 and by the ERS Executive Committee, June 2001. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2002;165(2):277–304. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.165.2.ats01. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources