Nanoparticle based insulin delivery system: the next generation efficient therapy for Type 1 diabetes
- PMID: 26498972
- PMCID: PMC4619439
- DOI: 10.1186/s12951-015-0136-y
Nanoparticle based insulin delivery system: the next generation efficient therapy for Type 1 diabetes
Abstract
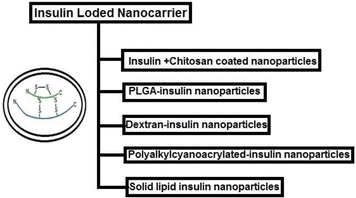
Diabetic cases have increased rapidly in recent years throughout the world. Currently, for type-1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM), multiple daily insulin (MDI) injections is the most popular treatment throughout the world. At this juncture, researchers are trying to develop different insulin delivery systems, especially through oral and pulmonary route using nanocarrier based delivery system. This next generation efficient therapy for T1DM may help to improve the quality of life of diabetic patients who routinely employ insulin by the subcutaneous route. In this paper, we have depicted various next generation nanocarrier based insulin delivery systems such as chitosan-insulin nanoparticles, PLGA-insulin nanoparticles, dextran-insulin nanoparticles, polyalkylcyanoacrylated-insulin nanoparticles and solid lipid-insulin nanoparticles. Modulation of these insulin nanocarriers may lead to successful oral or pulmonary insulin nanoformulations in future clinical settings. Therefore, applications and limitations of these nanoparticles in delivering insulin to the targeted site have been thoroughly discussed.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Oral Insulin: Myth or Reality.Curr Diabetes Rev. 2018;14(6):497-508. doi: 10.2174/1573399813666170621122742. Curr Diabetes Rev. 2018. PMID: 28637407 Review.
-
Polymer-based nanoparticles for oral insulin delivery: Revisited approaches.Biotechnol Adv. 2015 Nov 1;33(6 Pt 3):1342-54. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2015.02.010. Epub 2015 Feb 26. Biotechnol Adv. 2015. PMID: 25728065 Review.
-
pH-responsive nanoparticles shelled with chitosan for oral delivery of insulin: from mechanism to therapeutic applications.Acc Chem Res. 2012 Apr 17;45(4):619-29. doi: 10.1021/ar200234q. Epub 2012 Jan 11. Acc Chem Res. 2012. PMID: 22236133 Review.
-
Drug Delivery Systems for Diabetes Treatment.Curr Pharm Des. 2019;25(2):166-173. doi: 10.2174/1381612825666190306153838. Curr Pharm Des. 2019. PMID: 30848184 Review.
-
Nanoparticle strategies for the oral delivery of insulin.Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2008 Jan;5(1):45-68. doi: 10.1517/17425247.5.1.45. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2008. PMID: 18095928 Review.
Cited by
-
Engineering immunomodulatory biomaterials for type 1 diabetes.Nat Rev Mater. 2019 Jun;4(6):429-450. doi: 10.1038/s41578-019-0112-5. Epub 2019 May 17. Nat Rev Mater. 2019. PMID: 32617176 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis and Optimization of Chitosan Nanoparticles Loaded with L-Ascorbic Acid and Thymoquinone.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2018 Nov 7;8(11):920. doi: 10.3390/nano8110920. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30405074 Free PMC article.
-
Utilizing Multifaceted Approaches to Target Drug Delivery in the Brain: From Nanoparticles to Biological Therapies.Cureus. 2024 Sep 1;16(9):e68419. doi: 10.7759/cureus.68419. eCollection 2024 Sep. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39360065 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Improvement of Therapeutic Value of Quercetin with Chitosan Nanoparticle Delivery Systems and Potential Applications.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 7;24(4):3293. doi: 10.3390/ijms24043293. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36834702 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Advances in Insulin Therapy.Diabetes Technol Ther. 2020 Dec;22(12):929-936. doi: 10.1089/dia.2020.0065. Epub 2020 May 12. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2020. PMID: 32310681 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kuzuya T, Nakagawa S, Satoh J, Kanazawa Y, Iwamoto Y, Kobayashi M et al. Report of the Committee on the classification and diagnostic criteria of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2002;55(1):65–85. ([pii]: S0168822701003655). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical