Prognostic significance of Traf2- and Nck- interacting kinase (TNIK) in colorectal cancer
- PMID: 26499327
- PMCID: PMC4619995
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-015-1783-y
Prognostic significance of Traf2- and Nck- interacting kinase (TNIK) in colorectal cancer
Abstract
Background: The potential of expression profiling using microarray analysis as a tool to predict the prognosis for different types of cancer has been realized. This study aimed to identify a novel biomarker for colorectal cancer (CRC).
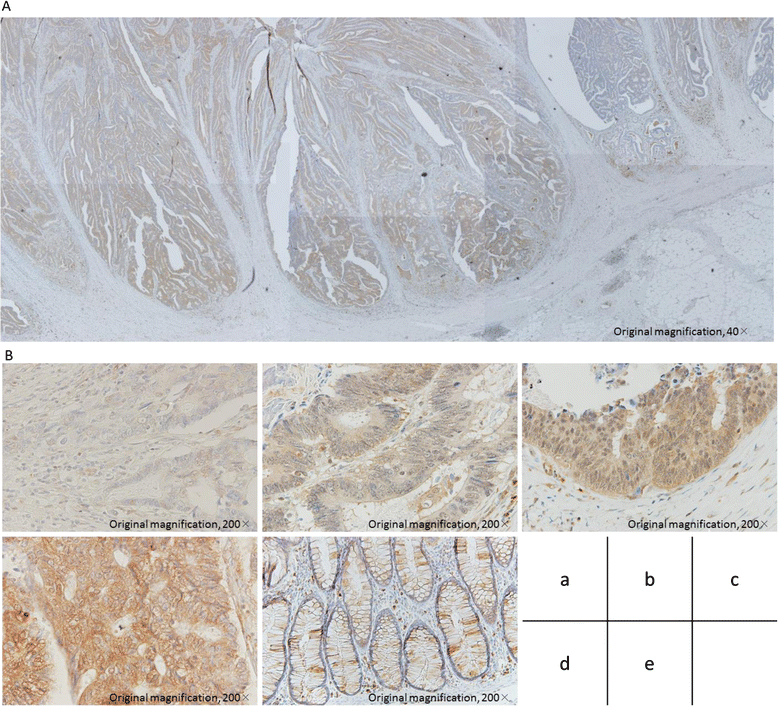
Methods: The expression profiles of cancer cells in 152 patients with stage I-III CRC were examined using microarray analysis. High expression in CRC cells, especially in patients with distant recurrences, was a prerequisite to select candidate genes. Thus, we identified seventeen candidate genes, and selected Traf2- and Nck-interacting kinase (TNIK), which was known to be associated with progression in CRC through Wnt signaling pathways. We analyzed the protein expression of TNIK using immunohistochemistry (IHC) and investigated the relationship between protein expression and patient characteristics in 220 stage I-III CRC patients.
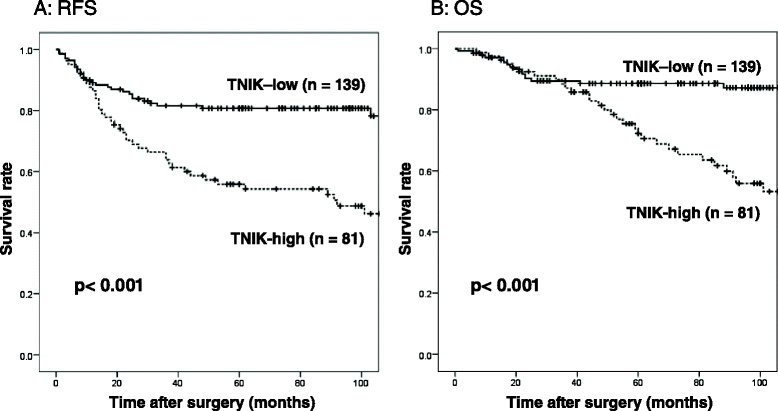
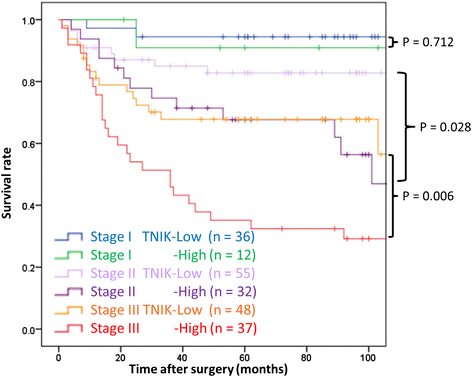
Results: Relapse-free survival was significantly worse in the TNIK high expression group than in the TNIK low expression group in stage II (p = 0.028) and stage III (p = 0.006) patients. In multivariate analysis, high TNIK expression was identified as a significant independent risk factor of distant recurrence in stage III patients.
Conclusion: This study is the first to demonstrate the prognostic significance of intratumoral TNIK protein expression in clinical tissue samples of CRC, in that high expression of TNIK protein in primary tumors was associated with distant recurrence in stage II and III CRC patients. This TNIK IHC study might contribute to practical decision-making in the treatment of these patients.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Nuclear expression of phosphorylated TRAF2- and NCK-interacting kinase in hepatocellular carcinoma is associated with poor prognosis.Pathol Res Pract. 2014 Oct;210(10):621-7. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2013.10.007. Epub 2014 Feb 24. Pathol Res Pract. 2014. PMID: 25160513
-
TNIK serves as a novel biomarker associated with poor prognosis in patients with pancreatic cancer.Tumour Biol. 2016 Jan;37(1):1035-40. doi: 10.1007/s13277-015-3881-5. Epub 2015 Aug 14. Tumour Biol. 2016. PMID: 26269113
-
Traf2- and Nck-interacting kinase is essential for Wnt signaling and colorectal cancer growth.Cancer Res. 2010 Jun 15;70(12):5024-33. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-0306. Epub 2010 Jun 8. Cancer Res. 2010. PMID: 20530691
-
Structural Insight into TNIK Inhibition.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 27;23(21):13010. doi: 10.3390/ijms232113010. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36361804 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emergence of TNIK inhibitors in cancer therapeutics.Cancer Sci. 2017 May;108(5):818-823. doi: 10.1111/cas.13203. Epub 2017 Apr 24. Cancer Sci. 2017. PMID: 28208209 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Harnessing the cyclization strategy for new drug discovery.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2022 Dec;12(12):4309-4326. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2022.09.022. Epub 2022 Oct 7. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2022. PMID: 36562004 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Engineered hydrogel reveals contribution of matrix mechanics to esophageal adenocarcinoma and identifies matrix-activated therapeutic targets.J Clin Invest. 2023 Dec 1;133(23):e168146. doi: 10.1172/JCI168146. J Clin Invest. 2023. PMID: 37788109 Free PMC article.
-
TNIK-driven regulation of ERK5 transcriptional activity in endothelial cells.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2025 Jul 2;12:1526676. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2025.1526676. eCollection 2025. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2025. PMID: 40672381 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of the ERG-regulated Kinome in Prostate Cancer Identifies TNIK as a Potential Therapeutic Target.Neoplasia. 2019 Apr;21(4):389-400. doi: 10.1016/j.neo.2019.02.005. Epub 2019 Mar 20. Neoplasia. 2019. PMID: 30901730 Free PMC article.
-
Construction of circRNA-based ceRNA network and its prognosis-associated subnet of clear cell renal cell carcinoma.Cancer Med. 2021 Nov;10(22):8210-8221. doi: 10.1002/cam4.4311. Epub 2021 Sep 27. Cancer Med. 2021. PMID: 34569727 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Foundation for Promotion of Cancer Research. Cancer statistics in Japan 2013. http://ganjoho.jp/professional/statistics/backnumber/2013_jp.html
-
- Shih W, Chetty R, Tsao MS. Expression profiling by microarrays in colorectal cancer (Review) Oncol Rep. 2005;13:517–24. - PubMed
-
- Kihara C, Tsunoda T, Tanaka T, Yamana H, Furukawa Y, Ono K, et al. Prediction of sensitivity of esophageal tumors to adjuvant chemotherapy by cDNA microarray analysis of gene-expression profiles. Cancer Res. 2001;61:6474–9. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

