small ORFs: A new class of essential genes for development
- PMID: 26500431
- PMCID: PMC4612599
- DOI: 10.1590/S1415-475738320150009
small ORFs: A new class of essential genes for development
Abstract
Genes that contain small open reading frames (smORFs) constitute a new group of eukaryotic genes and are expected to represent 5% of the Drosophila melanogaster transcribed genes. In this review we provide a historical perspective of their recent discovery, describe their general mechanism and discuss the importance of smORFs for future genomic and transcriptomic studies. Finally, we discuss the biological role of the most studied smORF so far, the Mlpt/Pri/Tal gene in arthropods. The pleiotropic action of Mlpt/Pri/Tal in D. melanogaster suggests a complex evolutionary scenario that can be used to understand the origins, evolution and integration of smORFs into complex gene regulatory networks.
Keywords: Drosophila; Tribolium; mlpt; pri; tarsal-less.
Figures
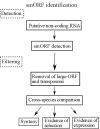
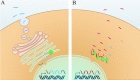
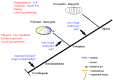
References
-
- Abouheif E, Fave MJ, Ibarraran-Viniegra AS, Lesoway MP, Rafiqi AM, Rajakumar R. Eco-evo-devo: The time has come. Adv Exp Med Biology. 2014;781:107–125. - PubMed
-
- Chanut-Delalande H, Hashimoto Y, Pelissier-Monier A, Spokony R, Dib A, Kondo T, Bohere J, Niimi K, Latapie Y, Inagaki S, et al. Pri peptides are mediators of ecdysone for the temporal control of development. Nat Cell Biol. 2014;16:1035–1044. - PubMed
-
- Delon I, Chanut-Delalande H, Payre F. The Ovo/Shavenbaby transcription factor specifies actin remodelling during epidermal differentiation in Drosophila . Mech Dev. 2003;120:747–758. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
