Neurogenesis paradoxically decreases both pattern separation and memory interference
- PMID: 26500511
- PMCID: PMC4593858
- DOI: 10.3389/fnsys.2015.00136
Neurogenesis paradoxically decreases both pattern separation and memory interference
Abstract
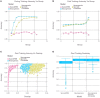
The hippocampus has been the focus of memory research for decades. While the functional role of this structure is not fully understood, it is widely recognized as being vital for rapid yet accurate encoding and retrieval of associative memories. Since the discovery of adult hippocampal neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus by Altman and Das in the 1960's, many theories and models have been put forward to explain the functional role it plays in learning and memory. These models postulate different ways in which new neurons are introduced into the dentate gyrus and their functional importance for learning and memory. Few if any previous models have incorporated the unique properties of young adult-born dentate granule cells and the developmental trajectory. In this paper, we propose a novel computational model of the dentate gyrus that incorporates the developmental trajectory of the adult-born dentate granule cells, including changes in synaptic plasticity, connectivity, excitability and lateral inhibition, using a modified version of the Restricted Boltzmann machine. Our results show superior performance on memory reconstruction tasks for both recent and distally learned items, when the unique characteristics of young dentate granule cells are taken into account. Even though the hyperexcitability of the young neurons generates more overlapping neural codes, reducing pattern separation, the unique properties of the young neurons nonetheless contribute to reducing retroactive and proactive interference, at both short and long time scales. The sparse connectivity is particularly important for generating distinct memory traces for highly overlapping patterns that are learned within the same context.
Keywords: computational modeling; dentate gyrus; neurogenesis; restricted Boltzmann machines; sparse coding.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Experience-Dependent Regulation of Dentate Gyrus Excitability by Adult-Born Granule Cells.J Neurosci. 2015 Aug 19;35(33):11656-66. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0885-15.2015. J Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26290242 Free PMC article.
-
A computational principle for hippocampal learning and neurogenesis.Hippocampus. 2005;15(6):722-38. doi: 10.1002/hipo.20095. Hippocampus. 2005. PMID: 15986407
-
A combination of running and memantine increases neurogenesis and reduces activation of developmentally-born dentate granule neurons in rats.Behav Brain Res. 2019 Oct 17;372:112005. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2019.112005. Epub 2019 Jun 2. Behav Brain Res. 2019. PMID: 31167109
-
Adult-born neurons add flexibility to hippocampal memories.Front Neurosci. 2023 Feb 15;17:1128623. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1128623. eCollection 2023. Front Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 36875670 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Paradox of pattern separation and adult neurogenesis: A dual role for new neurons balancing memory resolution and robustness.Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2016 Mar;129:60-8. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2015.10.013. Epub 2015 Nov 6. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2016. PMID: 26549627 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of High-Intensity Interval Training Protocols on Blood Lactate Levels and Cognition in Healthy Adults: Systematic Review and Meta-Regression.Sports Med. 2023 May;53(5):977-991. doi: 10.1007/s40279-023-01815-2. Epub 2023 Mar 14. Sports Med. 2023. PMID: 36917435
-
The impact of adult neurogenesis on affective functions: of mice and men.Mol Psychiatry. 2024 Aug;29(8):2527-2542. doi: 10.1038/s41380-024-02504-w. Epub 2024 Mar 18. Mol Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 38499657 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neurogenic Effects of Low-Dose Whole-Body HZE (Fe) Ion and Gamma Irradiation.Radiat Res. 2016 Dec;186(6):614-623. doi: 10.1667/RR14530.1. Epub 2016 Dec 1. Radiat Res. 2016. PMID: 27905869 Free PMC article.
-
Memory Traces Diminished by Exercise Affect New Learning as Proactive Facilitation.Front Neurosci. 2020 Mar 10;14:189. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2020.00189. eCollection 2020. Front Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32210755 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of adult-born immature granule cells on pattern separation in the hippocampal dentate gyrus.Cogn Neurodyn. 2024 Aug;18(4):2077-2093. doi: 10.1007/s11571-023-09985-5. Epub 2023 Jul 1. Cogn Neurodyn. 2024. PMID: 39104672 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Altman J., Das G. D. (1965). Post-natal origin of microNeurons in the rat brain. Nature 207, 953–956. - PubMed
-
- Altman J., Das G. (1967). Postnatal neurogenesis in the guinea-pig. Nature 214, 1098–1101. - PubMed
-
- Barnes C. A., McNaughton B. L., Mizumori S. J., Leonard B. W., Lin L. H. (1990). Comparison of spatial and temporal characteristics of Neuronal activity in sequential stages of hippocampal processing. Prog. Brain Res. 83, 287–300. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

