Training Efficiency and Transfer Success in an Extended Real-Time Functional MRI Neurofeedback Training of the Somatomotor Cortex of Healthy Subjects
- PMID: 26500521
- PMCID: PMC4598802
- DOI: 10.3389/fnhum.2015.00547
Training Efficiency and Transfer Success in an Extended Real-Time Functional MRI Neurofeedback Training of the Somatomotor Cortex of Healthy Subjects
Abstract
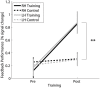
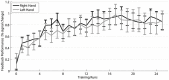
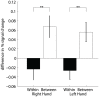
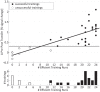
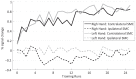
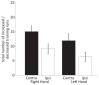
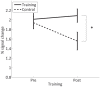
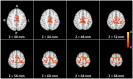
This study investigated the level of self-regulation of the somatomotor cortices (SMCs) attained by an extended functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) neurofeedback training. Sixteen healthy subjects performed 12 real-time functional magnetic resonance imaging neurofeedback training sessions within 4 weeks, involving motor imagery of the dominant right as well as the non-dominant left hand. Target regions of interests in the SMC were individually localized prior to the training by overt finger movements. The feedback signal (FS) was defined as the difference between fMRI activation in the contra- and ipsilateral SMC and visually presented to the subjects. Training efficiency was determined by an off-line general linear model analysis determining the fMRI percent signal changes in the SMC target areas accomplished during the neurofeedback training. Transfer success was assessed by comparing the pre- and post-training transfer task, i.e., the neurofeedback paradigm without the presentation of the FS. Group results show a distinct increase in feedback performance (FP) in the transfer task for the trained group compared to a matched untrained control group, as well as an increase in the time course of the training, indicating an efficient training and a successful transfer. Individual analysis revealed that the training efficiency was not only highly correlated to the transfer success but also predictive. Trainings with at least 12 efficient training runs were associated with a successful transfer outcome. A group analysis of the hemispheric contributions to the FP showed that it is mainly driven by increased fMRI activation in the contralateral SMC, although some individuals relied on ipsilateral deactivation. Training and transfer results showed no difference between left- and right-hand imagery, with a slight indication of more ipsilateral deactivation in the early right-hand trainings.
Keywords: human; motor cortex; neurofeedback; real-time fMRI; somatosensory cortex.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Higher-order Brain Areas Associated with Real-time Functional MRI Neurofeedback Training of the Somato-motor Cortex.Neuroscience. 2018 May 15;378:22-33. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2016.04.034. Epub 2016 Apr 29. Neuroscience. 2018. PMID: 27133575 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Motor Imagery and Visual Neurofeedback on Activation in the Swallowing Network: A Real-Time fMRI Study.Dysphagia. 2019 Dec;34(6):879-895. doi: 10.1007/s00455-019-09985-w. Epub 2019 Feb 15. Dysphagia. 2019. PMID: 30771088 Free PMC article.
-
Self-regulation of inter-hemispheric visual cortex balance through real-time fMRI neurofeedback training.Neuroimage. 2014 Oct 15;100:1-14. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2014.05.072. Epub 2014 Jun 4. Neuroimage. 2014. PMID: 24904993
-
Meta-analysis of real-time fMRI neurofeedback studies using individual participant data: How is brain regulation mediated?Neuroimage. 2016 Jan 1;124(Pt A):806-812. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2015.09.042. Epub 2015 Sep 28. Neuroimage. 2016. PMID: 26419389 Review.
-
A Guide to Literature Informed Decisions in the Design of Real Time fMRI Neurofeedback Studies: A Systematic Review.Front Hum Neurosci. 2020 Feb 25;14:60. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2020.00060. eCollection 2020. Front Hum Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32161529 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Brain Networks Underlying Strategy Execution and Feedback Processing in an Efficient Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging Neurofeedback Training Performed in a Parallel or a Serial Paradigm.Front Hum Neurosci. 2021 May 25;15:645048. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2021.645048. eCollection 2021. Front Hum Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34113243 Free PMC article.
-
Automated semi-real-time detection of muscle activity with ultrasound imaging.Med Biol Eng Comput. 2021 Sep;59(9):1961-1971. doi: 10.1007/s11517-021-02407-w. Epub 2021 Aug 16. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2021. PMID: 34398417 Free PMC article.
-
Self-Regulation of the Fusiform Face Area in Autism Spectrum: A Feasibility Study With Real-Time fMRI Neurofeedback.Front Hum Neurosci. 2019 Dec 20;13:446. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2019.00446. eCollection 2019. Front Hum Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31920602 Free PMC article.
-
Rt-fMRI neurofeedback-guided cognitive reappraisal training modulates amygdala responsivity in posttraumatic stress disorder.Neuroimage Clin. 2020;28:102483. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2020.102483. Epub 2020 Oct 28. Neuroimage Clin. 2020. PMID: 33395974 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Modulating the interhemispheric activity balance in the intraparietal sulcus using real-time fMRI neurofeedback: Development and proof-of-concept.Neuroimage Clin. 2020;28:102513. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2020.102513. Epub 2020 Nov 27. Neuroimage Clin. 2020. PMID: 33396000 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Auer T., Frahm J. (2009). Functional MRI using one- and two-threshold approaches in SPM5. Neuroimage 47, S102.10.1016/S1053-8119(09)70881-X - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

