Association of Statins with Sensory and Autonomic Ganglionopathy
- PMID: 26500548
- PMCID: PMC4595790
- DOI: 10.3389/fnagi.2015.00191
Association of Statins with Sensory and Autonomic Ganglionopathy
Abstract
Objective: To examine if statins have an effect on small nerve fibers.
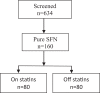
Methods: This retrospective study evaluated the effect of statins in pure small-fiber neuropathy (SFN). Outcome measures were symptom scales (numbness, tingling, and autonomic symptoms), skin biopsies assessing epidermal nerve fiber density (ENFD), sweat gland nerve fiber density (SGNFD), and quantitative autonomic testing.
Results: One hundred and sixty participants with pure SFN were identified. Eighty participants (women/men, age ± SD 33/47, 68.1 ± 11.6 years old) were on statins for 53.5 ± 28.7 months to treat dyslipidemia and they were age and gender matched with 80 participants (33/47, 68.1 ± 9.5) that were off statins. ANOVA showed reduced ENFD/SGNFD at the proximal leg in the statin group [(count/mm) 8.3 ± 3.6/51.3 ± 14.2] compared to the off statin group (10.4 ± 3.8, p = 0.0008/56.4 ± 12.7, p = 0.018). There was no difference in ENFD/SGNFD at the distal leg in the statin group (4.9 ± 3.2/39.8 ± 15.7) compared to the off statin group (5.9 ± 3.4, p = 0.067/41.8 ± 15.9, p = 0.426). Statins did not affect symptom scales and the outcome of autonomic testing.
Conclusion: Statin use is associated with degeneration of sensory and autonomic fibers. The pattern of abnormalities, e.g., degeneration of proximal while sparing of distal fibers, is consistent with a non-length-dependent process with lesions in the dorsal root and the autonomic ganglia. The statin-associated sensory and autonomic ganglionopathy is mild.
Keywords: ganglionopathy; neuronopathy; small-fiber neuropathy; statin toxicity; statins.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Diagnostic Accuracy of Electrochemical Skin Conductance in the Detection of Sudomotor Fiber Loss.Front Neurol. 2020 Apr 17;11:273. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2020.00273. eCollection 2020. Front Neurol. 2020. PMID: 32425871 Free PMC article.
-
Electrochemical Skin Conductance Correlates with Skin Nerve Fiber Density.Front Aging Neurosci. 2016 Aug 24;8:199. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2016.00199. eCollection 2016. Front Aging Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27605912 Free PMC article.
-
Association of small fiber neuropathy and post treatment Lyme disease syndrome.PLoS One. 2019 Feb 12;14(2):e0212222. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0212222. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 30753241 Free PMC article.
-
[Autoimmune autonomic ganglionopathy and acute autonomic and sensory neuropathy].Rinsho Shinkeigaku. 2013;53(11):1326-9. doi: 10.5692/clinicalneurol.53.1326. Rinsho Shinkeigaku. 2013. PMID: 24291976 Review. Japanese.
-
Non-length-dependent small fiber neuropathy: Not a matter of stockings and gloves.Muscle Nerve. 2022 Jan;65(1):10-28. doi: 10.1002/mus.27379. Epub 2021 Aug 9. Muscle Nerve. 2022. PMID: 34374103 Review.
Cited by
-
Study on risk factors of diabetic peripheral neuropathy and establishment of a prediction model by machine learning.BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2023 Aug 2;23(1):146. doi: 10.1186/s12911-023-02232-1. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2023. PMID: 37533059 Free PMC article.
-
Association of Serum Cholesterol Levels With Peripheral Nerve Damage in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes.JAMA Netw Open. 2019 May 3;2(5):e194798. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2019.4798. JAMA Netw Open. 2019. PMID: 31150078 Free PMC article.
-
Burning Mouth Syndrome From Statin Use: A Case Study.Cureus. 2024 Dec 6;16(12):e75223. doi: 10.7759/cureus.75223. eCollection 2024 Dec. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39759742 Free PMC article.
-
Magnetic Resonance Imaging as a Biomarker in Diabetic and HIV-Associated Peripheral Neuropathy: A Systematic Review-Based Narrative.Front Neurosci. 2021 Sep 21;15:727311. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.727311. eCollection 2021. Front Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34621152 Free PMC article.
-
Sensory Neuronopathies.Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2017 Aug 23;17(10):79. doi: 10.1007/s11910-017-0784-4. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28836102 Review.
References
-
- Birnbaum J., Bingham C. O., III (2014). Non-length-dependent and length-dependent small-fiber neuropathies associated with tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-inhibitor therapy in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: expanding the spectrum of neurological disease associated with TNF-inhibitors. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 43, 638–647.10.1016/j.semarthrit.2013.10.007 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous