Interdisciplinary, interinstitutional and international collaboration of family medicine researchers in Taiwan
- PMID: 26500827
- PMCID: PMC4614802
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.1321
Interdisciplinary, interinstitutional and international collaboration of family medicine researchers in Taiwan
Abstract
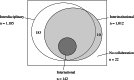
The family medicine researches flourished worldwide in the past decade. However, the collaborative patterns of family medicine publications had not been reported. Our study analyzed the collaborative activity of family medicine researchers in Taiwan. We focused on the types of collaboration among disciplines, institutions and countries. We searched "family medicine" AND "Taiwan" in address field from Web of Science and documented the disciplines, institutions and countries of all authors. We analyzed the collaborative patterns of family medicine researchers in Taiwan from 2010 to 2014. The journal's impact factor of each article in the same publication year was also retrieved. Among 1,217 articles from 2010 to 2014, interdisciplinary collaboration existed in 1,185 (97.3%) articles, interinstitutional in 1,012 (83.2%) and international in 142 (11.7%). Public health was the most common collaborative discipline. All international researches were also interdisciplinary and interinstitutional. The United States (75 articles), the United Kingdom (21) and the People's Republic of China (20) were the top three countries with which family medicine researchers in Taiwan had collaborated. We found a high degree of interdisciplinary and interinstitutional collaboration of family medicine researches in Taiwan. However, the collaboration of family medicine researchers in Taiwan with family medicine colleagues of other domestic or foreign institutions was insufficient. The future direction of family medicine studies could focus on the promotion of communication among family medicine researchers.
Keywords: Collaboration; Family medicine; Research; Taiwan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare there are no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
International collaboration of clinical medicine research in Taiwan, 1990-2004: a bibliometric analysis.J Chin Med Assoc. 2007 Mar;70(3):110-6. doi: 10.1016/S1726-4901(09)70340-5. J Chin Med Assoc. 2007. PMID: 17389155
-
From the History of the Croatian Dermatovenereological Society - The Croatian Medical Association and an Overview of Important Information Regarding the Journal Acta Dermatovenerologica Croatica.Acta Dermatovenerol Croat. 2018 Dec;26(4):344-348. Acta Dermatovenerol Croat. 2018. PMID: 30665489
-
Family medicine publications in Taiwan: an analysis of the Web of Science database from 1993 to 2012.J Chin Med Assoc. 2014 Nov;77(11):583-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jcma.2014.05.015. Epub 2014 Sep 18. J Chin Med Assoc. 2014. PMID: 25238712
-
Assessing the evolution of scientific publications in orthopedics journals from mainland China, Hong Kong, and Taiwan: a 12-year survey of the literature.J Orthop Surg Res. 2016 Jun 17;11(1):69. doi: 10.1186/s13018-016-0404-z. J Orthop Surg Res. 2016. PMID: 27317092 Free PMC article. Review.
-
China's Contribution to Anesthesiology Research: A 10-Year Survey of the Literature.Anesth Analg. 2016 May;122(5):1640-5. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0000000000001225. Anesth Analg. 2016. PMID: 27003916 Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous