Specific Language Impairment, Nonverbal IQ, Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder, Autism Spectrum Disorder, Cochlear Implants, Bilingualism, and Dialectal Variants: Defining the Boundaries, Clarifying Clinical Conditions, and Sorting Out Causes
- PMID: 26502218
- PMCID: PMC4867925
- DOI: 10.1044/2015_JSLHR-L-15-0255
Specific Language Impairment, Nonverbal IQ, Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder, Autism Spectrum Disorder, Cochlear Implants, Bilingualism, and Dialectal Variants: Defining the Boundaries, Clarifying Clinical Conditions, and Sorting Out Causes
Abstract
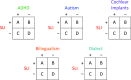
Purpose: The purpose of this research forum article is to provide an overview of a collection of invited articles on the topic "specific language impairment (SLI) in children with concomitant health conditions or nonmainstream language backgrounds." Topics include SLI, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, autism spectrum disorder, cochlear implants, bilingualism, and dialectal language learning contexts.
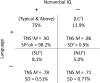
Method: The topic is timely due to current debates about the diagnosis of SLI. An overarching comparative conceptual framework is provided for comparisons of SLI with other clinical conditions. Comparisons of SLI in children with low-normal or normal nonverbal IQ illustrate the unexpected outcomes of 2 × 2 comparison designs.
Results: Comparative studies reveal unexpected relationships among speech, language, cognitive, and social dimensions of children's development as well as precise ways to identify children with SLI who are bilingual or dialect speakers.
Conclusions: The diagnosis of SLI is essential for elucidating possible causal pathways of language impairments, risks for language impairments, assessments for identification of language impairments, linguistic dimensions of language impairments, and long-term outcomes. Although children's language acquisition is robust under high levels of risk, unexplained individual variations in language acquisition lead to persistent language impairments.
Figures
References
-
- American Psychiatric Association. (1994). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (4th ed.). Washington, DC: Author.
-
- American Psychiatric Association. (2013). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (5th ed.). Washington, DC: Author.
-
- Archibald L. M. D., & Joaanisse M. F. (2009). On the sensitivity and specificity of nonword repetition and sentence recall to language and memory impairments in children. Journal of Speech, Language, and Hearing Research, 52, 899–914. - PubMed
-
- Cardy J. E. O., Tannock R., Johnson A., & Johnson C. J. (2010). The contributions of processing impairments to SLI: Insights from attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Journal of Communication Disorders, 43, 77–91. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

