Genetic association analyses implicate aberrant regulation of innate and adaptive immunity genes in the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus
- PMID: 26502338
- PMCID: PMC4668589
- DOI: 10.1038/ng.3434
Genetic association analyses implicate aberrant regulation of innate and adaptive immunity genes in the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus
Abstract
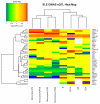
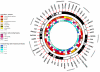
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a genetically complex autoimmune disease characterized by loss of immune tolerance to nuclear and cell surface antigens. Previous genome-wide association studies (GWAS) had modest sample sizes, reducing their scope and reliability. Our study comprised 7,219 cases and 15,991 controls of European ancestry, constituting a new GWAS, a meta-analysis with a published GWAS and a replication study. We have mapped 43 susceptibility loci, including ten new associations. Assisted by dense genome coverage, imputation provided evidence for missense variants underpinning associations in eight genes. Other likely causal genes were established by examining associated alleles for cis-acting eQTL effects in a range of ex vivo immune cells. We found an over-representation (n = 16) of transcription factors among SLE susceptibility genes. This finding supports the view that aberrantly regulated gene expression networks in multiple cell types in both the innate and adaptive immune response contribute to the risk of developing SLE.
Figures
References
-
- Deapen D, et al. A revised estimate of twin concordance in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1992;35:311–318. - PubMed
-
- Alarcón-Segovia D, et al. Familial aggregation of systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, and other autoimmune diseases in 1,177 lupus patients from the GLADEL cohort. Arthritis Rheum. 2005;52:1138–1147. - PubMed
-
- Hom G, et al. Association of systemic lupus erythematosus with C8orf13-BLK and ITGAM-ITGAX. New Engl. J. Med. 2008;358:900–909. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
- 085492/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R01 CA133996/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R37HL039693/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 5R01CA133996/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 HL039693/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 19289/ARC_/Arthritis Research UK/United Kingdom
- P50 CA093459/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01HG004446/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- RC4 AG039029/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RC4AG039029/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- 5R01ES011740/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG004446/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA097007/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG009740/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- 3P50CA093459/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- 5P50CA097007/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 ES011740/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- U01AG009740/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- 19289/VAC_/Versus Arthritis/United Kingdom
- 051276/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- RC2 AG036495/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- 94825/CAPMC/ CIHR/Canada
- RC2AG036495/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

